Что присходит с опционами на бумаги США, если андерлаинг участвует в слиянии за наличные?
Если опцион на акцию связан со слиянием, при котором базисная ценная бумага была конвертирована в наличные средства в 100%-ном размере после 31 декабря 2007 года, Корпорация OCC ускорит срок его истечения. Новая дата экспирации для таких опционов будет перенесена на ближайший день обычной экспирации акций, за исключением случаев, когда конверсия в наличные происходит позже вторника недели экспирации – тогда дата экспирации для всех контрактов, у которых срок истечения не на этой неделе, будет перенесена на дату экспирации в следующем месяце.
Обратите внимание, что данное ускорение не влияет на порог автоматического исполнения, согласно которому OCC автоматически исполняет все опционы со страйк-ценой "в деньгах" хотя бы на $0,01. Оно также не влияет на дату денежного расчета такого исполнения (режимом расчета остается T+2).
Также обращаем внимание, что данное ускорение не затрагивает опционы, которые были конвертированы в денежные средства 31 декабря 2007 года или ранее. Такие опционные серии остаются активными до изначальной даты экспирации.
U.S. Securities Options Exercise Limits
INTRODUCTION
Option exercise limits, along with position limits (See KB1252), have been in place since the inception of standardized trading of U.S. securities options. Their purpose is to prevent manipulative actions in underlying securities (e.g., corners or squeezes) as well as disruptions in option markets where illiquidity in a given option class exists. These limits serve to prohibit an account, along with its related accounts, from cumulatively exercising within any five consecutive business day period, a number of options contracts in excess of the defined limit for a given equity options class (i.e., option contracts associated with a particular underlying security). This includes both early exercises and expiration exercises.
OVERVIEW
U.S. securities option exercise limits are established by FINRA and the U.S. options exchanges. The exercise limits are generally the same as position limits and they can vary by option class as they take into consideration factors such as the number of shares outstanding and trading volume of the underlying security. Limits are also subject to adjustment and therefore can vary over time. The Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), the central clearinghouse for U.S. exchange traded securities options, publishes a daily file with these limits on its public website. The link is as follows: http://www.optionsclearing.com/webapps/position-limits. FINRA Rule 2360(b)(4) addresses exercise limits and can be found via the following website link: http://finra.complinet.com/en/display/display.html?rbid=2403&record_id=16126&element_id=6306&highlight=2360#r16126).
Note that exercise limits are applied based upon the the side of the market represented by the option position. Accordingly, all exercises of call options over the past five business days are aggregated for purposes of determining the limit for the purposes of purchasing the underlying security. Similarly, a separate computation whereby all put exercises over the past five business days are aggregated is required for purposes of determining sales of the underlying.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
It's important to note that while exercise limits may be set at levels identical to position limits, it is possible for an account holder to reach an exercise limit without violating positions limits for a given option class. This is because exercise limits are cumulative and one could conceivably purchase options up to the position limit, exercise those options and purchase additional options which, if allowed to be exercised within the five business day window, would exceed the limit.
Account holders are responsible for monitoring their cumulative options exercises as well as the exercise limit quantities to ensure compliance. In addition, IB reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of any options, regardless of their intrinsic value or remaining maturity, if the effect of that exercise would be to violate the exercise limit rule.
How Can I Lapse Long Options?
Account holders have the ability to lapse equity options (also known as providing contrary intentions) they hold long in their account.
From Trader Workstation, go to the Trade menu and select Option Exercise.
The Option Exercise window will appear and any long options you are holding will populate under the Long Positions column header. To lapse one of them, left-click on the light blue “Select” link under the Exercise Option column header for that particular option.
.bmp)
Select “Lapse” from the drop down menu.
.bmp)
Review the request, and click the blue “ T” Transmit button to submit the lapse request.
.bmp)
The Option Exercise Confirmation window will appear and will show how much the option is in-the-money. If the option is out-of-the-money, a warning message will appear. To submit the Lapse request, click the Override and Transmit button.
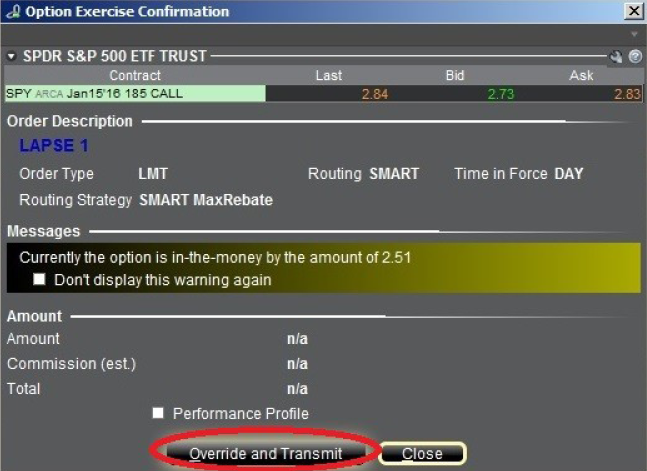
Your Lapse request will now show as an order line on your Trader Workstation until the clearinghouse processes the request.
Unless the lapse request is final it is still considered a position in the credit system and subject to the expiration exposure calculations. The Orders page of Global Configuration provides a selection box where you can specify that an option exercise request be final, and therefore cannot be canceled or editable until the cutoff time (default), which varies by clearing house. To specify this parameter, from the Mosaic File menu or Classic Edit menu, select Global Configuration and go to Orders followed by Settings from the configuration tree on the left side. Make your selection using the “Option exercise requests are” drop down menu. Please note that some contracts will not follow this rule and will remain revocable up until the clearing house deadline.
In the event that an option exercise cannot be submitted via the TWS, an option exercise request with all pertinent details (including option symbol, account number and exact quantity), should be created in a ticket via the Account Management window. In the Account Management window, click on "Inquiry/Problem Ticket". The ticket should include the words "Option Exercise Request" in the subject line. Please provide a contact number and clearly state in your ticket why the TWS Option Exercise window was not available for use.
Option Lapse Requests (whether received through the TWS Option Exercise window or by a ticket sent via Account Management/Message Center) must be submitted as follows:
Note: "Contrary intentions" are handled on a best efforts basis.
Особенности исполнения опционов "колл" до истечения
ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Исполнение опциона "колл" на акции не представляет экономической выгоды, поскольку:
- Оно приводит к утрате остаточной временной стоимости опциона;
- Требует большего объема капитала для оплаты или финансирования поставок; а также
- Может подвергнуть владельца опциона повышенному риску убытков по акциям относительно суммы премии опциона.
Тем не менее, запрос досрочного исполнения американского опциона "колл" для получения дивидендов может быть выгоден тем трейдерам, которые в состоянии удовлетворить повышенным требованиям размера капитала или займа и готовы к риску крупных потерь.
УСЛОВИЯ
Для справки, у владельца опциона "колл" нет права получать дивиденды по базовой акции, поскольку они начисляются только акционерам в день объявления дивидендов. При равенстве остальных условий, цена акций должна уменьшиться на сумму, которую составляют дивиденды в экс-дивидендную дату. И хотя теория ценообразования опционов предполагает, что цена "колл" будет отражать дисконтированную стоимость ожидаемых дивидендов, выплачиваемых в течение действия контракта, она также может упасть в вышеупомянутую дату. Такое развитие событий наиболее вероятно, а досрочное исполнение выгодно при условии, что:
1. Опцион глубоко "в деньгах" и значение дельта равно 100;
2. Временная стоимость опциона низкая или отсутствует;
3. Сумма дивидендов относительно высока и экс-дивидендная дата предшествует дате истечения.
ПРИМЕРЫ
Чтобы продемонстрировать влияние таких условий на решение о досрочном исполнении, возьмем счет с длинным наличным балансом в $9000 и длинной позицией "колл" по воображаемой акции “ABC” с ценой страйка $90,00 и 10-ю днями до истечения. На данный момент торги ABC проходят по цене $100,00, объявленные дивиденды составляют $2.00 за акцию, а экс-дивидендная дата наступает завтра. Также предположим, что у цены опциона и цены акции схожее поведение и они обе снижаются на сумму дивидендов в экс-дивидендную дату.
Рассмотрим решение об исполнении с намерением сохранить значение дельта (100) у позиции по акциям и увеличить общий капитал, используя два предположения о цене опциона: согласно одному он будет продан по паритету (номинальной стоимости), а другому - выше паритета.
СЦЕНАРИЙ 1: Паритетная цена опциона ($10,00)
Если у опциона паритетная цена, то досрочное исполнение поможет сохранить дельта позиции и избежать снижения стоимости длинного опциона при торговле в экс-дивидендную дату. При таком раскладе вся денежная прибыль используется для покупки акций по цене страйка, опцион утрачивает премию, а акции, чистый дивиденд и дивиденды к получению перечисляются на счет. Такого же конечного результата можно достичь, продав опцион до экс-дивидендной даты и купив акции (не забудьте учесть комиссии/спреды):
| СЦЕНАРИЙ 1 | ||||
|
Компоненты счета |
Начальный баланс |
Досрочное исполнение |
Без действия |
Продать опцион, купить акции |
| Наличные | $9 000 | $0 | $9 000 | $0 |
| Опционы | $1 000 | $0 | $800 | $0 |
| Акции | $0 | $9 800 | $0 | $9 800 |
| Дивиденды к получению | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Общий капитал | $10 000 | $10 000 | $9 800 | $10 000 минус комиссия/спред |
СЦЕНАРИЙ 2: Цена опциона выше паритета ($11.00)
Если цена опциона выше паритета, то досрочное исполнение для извлечения дивиденда может быть невыгодно. При таких условиях преждевременное исполнение приведет к убыткам в размере $100 от временной стоимости опциона, а продажа опциона и покупка акций может быть менее выгодна после вычета комиссии, нежели отсутствие мер. В данном случае предпочтительно бездействие.
| СЦЕНАРИЙ 2 | ||||
|
Компоненты счета |
Начальный баланс |
Досрочное исполнение |
Без действия |
Продать опцион, купить акции |
| Наличные | $9,000 | $0 | $9 000 | $100 |
| Опционы | $1 100 | $0 | $1 100 | $0 |
| Акции | $0 | $9 800 | $0 | $9 800 |
| Дивиденды к получению | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Общий капитал | $10 100 | $10 000 | $10 100 | $10 100 минус комиссия/спред |
![]() ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: Владельцам длинной позиции "колл", являющейся частью спреда, стоит обратить особое внимание на риски неисполнения длинного лега с учетом возможной переуступки короткого. Заметьте, что переуступка короткого "колла" приведет к образованию короткой позиции по акциям, владелец которой обязан выплачивать дивиденды в дату их объявления кредитору акций. Помимо этого, процедура клиринговых домов по обработке уведомлений об исполнении не поддерживает отправку уведомлений в ответ на уступку.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ: Владельцам длинной позиции "колл", являющейся частью спреда, стоит обратить особое внимание на риски неисполнения длинного лега с учетом возможной переуступки короткого. Заметьте, что переуступка короткого "колла" приведет к образованию короткой позиции по акциям, владелец которой обязан выплачивать дивиденды в дату их объявления кредитору акций. Помимо этого, процедура клиринговых домов по обработке уведомлений об исполнении не поддерживает отправку уведомлений в ответ на уступку.
Возьмем, к примеру, кредитный спред "колл" (медвежий) по SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY), состоящий из 100 коротких контрактов с ценой страйка $146 (13 марта) и 100 длинных контрактов с ценой страйка $147 (13 марта). 14 марта 2013 SPY Trust объявил о дивидендах в размере $0,69372 за акцию, которые подлежали выплате 30 апреля 2013 лицам, являющимся акционерами по состоянию на 19 марта 2013. Учитывая 3-хдневный расчетный период для акций США, купить акции или исполнить "колл" для получения дивидендов требовалось не позже 14 марта 2013, поскольку на следующий день торговля акциями стала происходить уже без дивиденда.
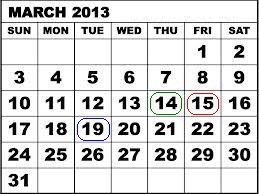
14 марта 2013 (за день до истечения) у двух опционных контрактов была паритетная цена, предполагающая риск в сумме $100 за контракт или $10 000 за позицию по 100 контрактам. Однако, несостоявшееся исполнение длинного контракта с целью извлечения дивидендов и избежания возможной переуступки коротких контрактов (лицами, так же желающими получить дивиденды), вылилось в дополнительный риск: $67,372 за контракт или $6737,20 за позицию с дивидендными обязательствами и уступленными короткими "коллами". Согласно таблице ниже, если бы короткий лег с опциона не был уступлен, то 15 марта 2013, при конечном расчете цен контракта, максимальный риск все еще составлял бы $100 за контракт.
| Дата | Цена закр. SPY | "Колл" $146, 13 марта | "Колл" $147 13 марта |
| 14 марта 2013 | $156,73 | $10,73 | $9,83 |
| 15 марта, 2013 | $155,83 | $9,73 | $8,83 |
Обращаем внимание, что если на Ваш счет распространяются требования о налоговых удержаниях согласно правилу 871(m) Министерства финансов США, то Вам может быть выгодно закрыть длинную опционную позицию до экс-дивидендной даты и повторно открыть ее после этой даты.
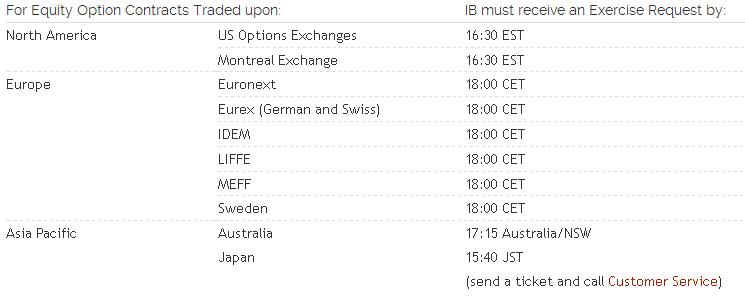
Подробности об отправке уведомления о досрочном исполнении можно найти здесь.
Вышеприведенная статья предоставлена исключительно в информационных целях и не является рекомендацией, торговым советом или заключением, что досрочное исполнение будет успешно и подойдет для всех клиентов и сделок. Владельцам счетов стоит проконсультироваться с налоговым специалистом, чтобы определить, к каким последствиям может привести досрочное исполнение, а также обратить особое внимание на риски замены длинной позиции по опционам на длинную по акциям.
Ликвидация по истечении
Вдобавок к политике принудительной ликвидации клиентских позиций в случае создавшегося дефицита маржи, IB также может ликвидировать позиции на основании истечения контрактов, которое может привести к излишнему риску и/или операционным сложностям. Примеры подобных случаев приведены ниже.
Исполнение опциона
IB оставляет за собой право запретить исполнение опционов на акции и/или закрыть позиции по ним, если их исполнение или назначение приведет к дефициту маржи. Несмотря на то, что покупка опциона, в основном, не требует маржи, поскольку позиция оплачивается полностью, владелец счета обязан либо целиком покрыть стоимость образовавшейся после исполнения длинной позиции по акциям (когда "колл" исполняется на наличном счете или у акций 100%-ная маржа), либо прoфинансировать длинную/короткую позицию по акциям (когда "колл"/"пут" исполняется на маржевом счете). Если на счете недостаточно средств до исполнения, то он подвергается избыточному риску в случае неблагоприятного изменения цены андарлаинга перед доставкой. Без финансовой защиты подобный риск ярко выражен и может сильно превзойти любую стоимость "в деньгах", имеющуюся у длинного опциона; особенно по истечении, когда клиринговые дома автоматически исполняют их, начиная уже с $0,01 за акцию.
Возьмем, к примеру, счет, капитал которого в 1-ый день составляет 20 длинных опционов "колл" (по гипотетическим акциям XYZ, цена которых при экспирации составляла $1 за контракт) с ценой страйка $50 и ценой андерлаинга $51. Предположим, что по Сценарию 1 опционы исполняются автоматически и цена акций XYZ во время открытия торговли во 2-ой день составляет $51. По Сценарию 2 тоже происходит автоматическое исполнение, но цена акций XYZ во время открытия торговли во 2-ой день составляет $48.
| Баланс счета | Перед истечением |
Сценарий 1: XYZ при открытии - $51 |
Сценарий 2: XYZ при открытии - $48 |
| Наличные |
$0,00 | ($100 000,00) | ($100 000,00) |
| Акции (длинн.) |
$0,00 | $102 000,00 | $96 000,00 |
|
Опцион* (длинн.) |
$2 000,00 | $0,00 | $0,00 |
| Чистый ликвидац. капитал/(дефицит) | $2 000,00 | $2 000,00 | ($4 000,00) |
| Требование маржи |
$0,00 | $25 500,00 | $25 500,00 |
| Избыток/(дефицит) маржи |
$0,00 | ($23 500,00) | ($29 500,00) |
*У длинных позиций по опционам нет кредитных средств.
Чтобы избежать подобных ситуаций, IB симулирует влияние предстоящего истечения, учитывая возможное смещение цен андерлаинга, и оценивает риск, которому подвергнется счет при потенциальной поставке. Если он будет сочтен избыточным, IB может: 1) ликвидировать опционы до исполнения; 2) позволить уступку опционов; и/или 3) разрешить поставку и сразу ликвидировать андерлаинг. Не исключено и ограничение возможности счета по открытию новых позиций во избежание повышения риска.
IB также оставляет за собой право ликвидировать позиции вечером, предшествующим расчетному дню, если, согласно прогнозу систем IB, расчет приведет к дефициту маржи. Чтобы избежать подобных ситуаций, IB симулирует влияние предстоящего истечения, учитывая возможное смещение цен андерлаинга, и оценивает риск, которому в итоге подвергнется каждый счет. К примеру, если по прогнозу IB расчет приведет к устранению позиций (напр., опционы истекут со статусом "вне денег" или опционы с наличным расчетом истекут "в деньгах"), то наши системы определят, как это скажется на марже.
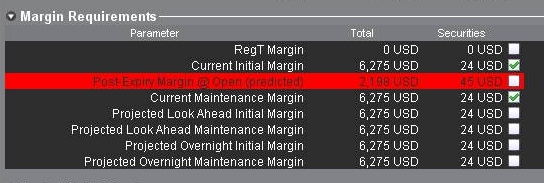
Если IB сочтет риск излишним, то позиции на Вашем счете могут быть ликвидированы, чтобы устранить прогнозируемый дефицит. Окно "Счет" в TWS содержит все необходимые показатели для отслеживания маржи. Прогнозируемый избыток отображен в строке "Маржа после истечения срока" (см. ниже); если его значение отрицательное и выделено красным цветом, то Ваш счет может подвергнуться принудительной ликвидации позиций. Расчеты этих показателей производятся за 3 дня до следующего истечения и обновляются примерно каждые 15 минут. Стоит отметить, что для иерархических счетовых структур (напр., с раздельным торговым лимитом) эта информация будет отображаться только на уровне мастер-счета, где все вычисления суммируются.
Обращаем внимание, что IB, как правило, инициирует ликвидацию, связанную с истечением, за 2 часа до закрытия торгов, но при этом может начать этот процесс раньше или позже, если на то есть причины. Приоритет ликвидации зависит от ряда показателей счета, включающего чистую ликвидационную стоимость, прогнозируемый дефицит после истечения, а также взаимосвязь между ценой страйка опциона и андерлаингом.
Фьючерсы с физической поставкой
За исключением отдельных контрактов, в основе которых лежит валюта, IB не разрешает клиентам получать или совершать поставки базового товара по фьючерсам с физическими расчетами или фьючерсным опционам. Во избежание поставок, позиции по истекающим фьючерсным контрактам следует перенести или закрыть до наступления сроков истечения (с их списком можно ознакомиться на сайте IB, выбрав "Поставка, исполнение и корпоративные действия" в меню "Торговля").
Обращаем Ваше внимание, что осведомленность о сроках закрытия является ответственностью владельца счета. IB может без дополнительного оповещения ликвидировать не закрытые вовремя позиции по контрактам с физической поставкой.
Информация о правилах физической поставки
У IBKR нет необходимых ресурсов для осуществления физической поставки большинства продуктов. Владельцы счетов с фьючерсными контрактами, исполняемыми посредством физических поставок базового товара, не могут выполнять или получать такие поставки.
Знание сроков закрытия каждого инструмента является ответственностью владельца счета. Если он своевременно не закрыл позицию по фьючерсному контракту с физической поставкой, то IBKR может без предупреждения ее ликвидировать. Обращаем внимание, что эта ликвидация никак не повлияет на активные ордера; владельцы счетов должны будут скорректировать закрывающие ордера, чтобы они соответствовали фактической позиции.
Во избежание поставок, позиции по истекающим фьючерсным контрактам следует перенести или закрыть до наступления срока истечения.
В таблице ниже перечислены сроки закрытия для контрактов на фьючерсы и фьючерсные опционы. Дату первого уведомления, первый день позиции и последнюю дату торгов можно узнать с помощью поиска контрактов на странице Поддержка на сайте IBKR. Эта информация предоставляется по мере возможностей, поэтому ее следует сверять с данными о контракте на сайте биржи.
Общие правила физической поставки по фьючерсам:
|
Контракт |
Разрешение на поставку |
Срок закрытия |
|
ZB, ZN, ZF (CBOT) |
Нет |
За 2 часа до конца открытых торгов в рабочий день, предшествующий первому дню уведомления (для длинных позиций), или последний день торговли (для коротких) |
|
Фьючерсы ZT (CBOT), японские гос. фьючерсы на облигации (JGB) |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до первого дня позиции (для длинных позиций) или конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до последнего дня торговли (для коротких). |
|
Фьючерсы EUREXUS |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня, предшествующего первому дню позиции (для длинных позиций), или последний день торговли (для коротких) |
|
2-летние облигации Jumbo EUREXUS (FTN2) и 3-летние фьючерсы на облигации (FTN3) |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до первого дня позиции (для длинных позиций) или последний день торговли (для коротких) |
|
Контракты IPE (GAS, NGS) |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до первого дня позиции (для длинных позиций) или за день до последнего дня торговли (для коротких) |
|
CME LIVE CATTLE (LE) |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до первого дня уведомления о намерении поставки (для длинных позиций) или последний день торговли (для коротких) |
|
CME NOK, SEK, PLZ, CZK, ILS, KRW, HUF и соответствующие ставки Euro |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 5 дней до последнего торгового дня как для длинных, так и для коротких позиций |
|
GBL, GBM, GBS, GBX (Eurex), CONF (Eurex) |
Нет |
За 2 часа до конца торгов в последний торговый день |
|
Валютные фьючерсы CME (EUR, GBP, CHF, AUD, CAD, JPY, HKD) |
Да* |
Не применимо* |
|
Фьючерсы Ethanol CME (ET) |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 5 дней до первого дня позиции (для длинных позиций) или последний день торговли (для коротких) |
| Фьючерсы NG (NYMEX) | Нет | Конец рабочего дня накануне первого дня позиции или последний день торговли – в зависимости от того, что наступит раньше (для длинных позиций), или конец рабочего дня накануне последнего дня торговли (для коротких) |
|
Другие контракты |
Нет |
Конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до первого дня позиции или последний день торговли – в зависимости от того, что наступит раньше (для длинных), или конец рабочего дня за 2 дня до последнего дня торговли (для коротких) |
*Поскольку на наличных и IRA-счетах нельзя держать иностранные валюты, то инструменты на этих счетах, выраженные в иностранной валюте, относятся к категории Другие контракты.
Общие правила физической поставки по фьючерсным опционам:
| Контракт | Разрешение на поставку | Срок закрытия |
| Все контракты | Да | Если дата истечения опциона предшествует первому дню позиции по фьючерсу, то по истечении опционы могут стать фьючерсами (или, в случае с опционами "вне денег", истечь с нулевой стоимостью). На появившийся фьючерс будут распространяться сроки закрытия, описанные выше. |
Considerations for Exercising Call Options Prior to Expiration
INTRODUCTION
Exercising an equity call option prior to expiration ordinarily provides no economic benefit as:
- It results in a forfeiture of any remaining option time value;
- Requires a greater commitment of capital for the payment or financing of the stock delivery; and
- May expose the option holder to greater risk of loss on the stock relative to the option premium.
Nonetheless, for account holders who have the capacity to meet an increased capital or borrowing requirement and potentially greater downside market risk, it can be economically beneficial to request early exercise of an American Style call option in order to capture an upcoming dividend.
BACKGROUND
As background, the owner of a call option is not entitled to receive a dividend on the underlying stock as this dividend only accrues to the holders of stock as of its dividend Record Date. All other things being equal, the price of the stock should decline by an amount equal to the dividend on the Ex-Dividend date. While option pricing theory suggests that the call price will reflect the discounted value of expected dividends paid throughout its duration, it may decline as well on the Ex-Dividend date. The conditions which make this scenario most likely and the early exercise decision favorable are as follows:
1. The option is deep-in-the-money and has a delta of 100;
2. The option has little or no time value;
3. The dividend is relatively high and its Ex-Date precedes the option expiration date.
EXAMPLES
To illustrate the impact of these conditions upon the early exercise decision, consider an account maintaining a long cash balance of $9,000 and a long call position in hypothetical stock “ABC” having a strike price of $90.00 and time to expiration of 10 days. ABC, currently trading at $100.00, has declared a dividend of $2.00 per share with tomorrow being the Ex-Dividend date. Also assume that the option price and stock price behave similarly and decline by the dividend amount on the Ex-Date.
Here, we will review the exercise decision with the intent of maintaining the 100 share delta position and maximizing total equity using two option price assumptions, one in which the option is selling at parity and another above parity.
SCENARIO 1: Option Price At Parity - $10.00
In the case of an option trading at parity, early exercise will serve to maintain the position delta and avoid the loss of value in long option when the stock trades ex-dividend, to preserve equity. Here the cash proceeds are applied in their entirety to buy the stock at the strike, the option premium is forfeited and the stock (net of dividend) and dividend receivable are credited to the account. If you aim for the same end result by selling the option prior to the Ex-Dividend date and purchasing the stock, remember to factor in commissions/spreads:
| SCENARIO 1 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $0 |
| Option | $1,000 | $0 | $800 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,000 | $10,000 | $9,800 | $10,000 less commissions/spreads |
SCENARIO 2: Option Price Above Parity - $11.00
In the case of an option trading above parity, early exercise to capture the dividend may not be economically beneficial. In this scenario, early exercise would result in a loss of $100 in option time value, while selling the option and buying the stock, after commissions, may be less beneficial than taking no action. In this scenario, the preferable action would be No Action.
| SCENARIO 2 | ||||
|
Account Components |
Beginning Balance |
Early Exercise |
No Action |
Sell Option & Buy Stock |
| Cash | $9,000 | $0 | $9,000 | $100 |
| Option | $1,100 | $0 | $1,100 | $0 |
| Stock | $0 | $9,800 | $0 | $9,800 |
| Dividend Receivable | $0 | $200 | $0 | $200 |
| Total Equity | $10,100 | $10,000 | $10,100 | $10,100 less commissions/spreads |
![]() NOTE:
NOTE:
Options have two components that make up their total premium value - intrinsic value and time value. The intrinsic value is the amount by which the option is in-the-money, while the time value represents the possibility that the option could become even more profitable before expiration as the underlying asset price fluctuates while providing protection against adverse moves.
Many options are American-style, which means they can be exercised early, ahead of their expiration date. Early exercise of an option eliminates the remaining time value component from the option's premium, since the option holder loses protection against unfavorable movements in the underlying asset’s price.
This makes early exercise suboptimal in most situations, as the option holder is willingly forfeiting a portion of the option's value.
There are a few specific circumstances where early exercise could make sense, such as:
- For call options on a stock that will pay dividends soon, where the dividend amount exceeds the remaining time value (and only if the exercise will settle on or prior to the record date for the dividend).
- For deep in-the-money options where the time value is negligible compared to the intrinsic value, and the option is expected to drop in value due to interest rate effects (PUTS), or expected stock loan benefits (CALLS).
The first case, exercising an in the money call immediately ahead of a dividend payment, is the most common economically-sensible early exercise. In most cases, it is advisable to hold or sell the option instead of exercising it early, in order to capture the remaining time value. An option should only be exercised early after carefully considering all factors and determining that the benefits of early exercise outweigh the time value being surrendered.
Account holders holding a long call position as part of a spread should pay particular attention to the risks of not exercising the long leg given the likelihood of being assigned on the short leg. Note that the assignment of a short call results in a short stock position and holders of short stock positions as of a dividend Record Date are obligated to pay the dividend to the lender of the shares. In addition, the clearinghouse processing cycle for exercise notices does not accommodate submission of exercise notices in response to assignment.
As example, consider a credit call (bear) spread on the SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY) consisting of 100 short contracts in the March '13 $146 strike and 100 long contracts in the March '13 $147 strike. On 3/14/13, with the SPY Trust declared a dividend of $0.69372 per share, payable 4/30/13 to shareholders of record as of 3/19/13. Given the 3 business day settlement time frame for U.S. stocks, one would have had to buy the stock or exercise the call no later than 3/14/13 in order receive the dividend, as the next day the stock began trading Ex-Dividend.

On 3/14/13, with one trading day left prior to expiration, the two option contracts traded at parity, suggesting maximum risk of $100 per contract or $10,000 on the 100 contract position. However, the failure to exercise the long contract in order to capture the dividend and protect against the likely assignment on the short contracts by others seeking the dividend created an additional risk of $67.372 per contract or $6,737.20 on the position representing the dividend obligation were all short calls assigned. As reflected on the table below, had the short option leg not been assigned, the maximum risk when the final contract settlement prices were determined on 3/15/13 would have remained at $100 per contract.
| Date | SPY Close | March '13 $146 Call | March '13 $147 Call |
| March 14, 2013 | $156.73 | $10.73 | $9.83 |
| March 15, 2013 | $155.83 | $9.73 | $8.83 |
Please note that if your account is subject to tax withholding requirements of the US Treasure rule 871(m), it may be beneficial to close a long option position before the ex-dividend date and re-open the position after ex-dividend.
For information regarding how to submit an early exercise notice please click here.
The above article is provided for information purposes only as is not intended as a recommendation, trading advice nor does it constitute a conclusion that early exercise will be successful or appropriate for all customers or trades. Account holders should consult with a tax specialist to determine what, if any, tax consequences may result from early exercise and should pay particular attention to the potential risks of substituting a long option position with a long stock position.
Expiration & Corporate Action Related Liquidations
In addition to the policy of force liquidating client positions in the event of a real-time margin deficiency, IBKR will also liquidate positions based upon certain expiration or corporate action related events which, after giving effect to, would create undue risk and/or operational concerns. Examples of such events are outlined below.
Option Exercise
IBKR reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of stock options and/or close short options if the effect of the exercise/assignment would be to place the account in margin deficit. While the purchase of an option generally requires no margin since the position is paid in full, once exercised the account holder is obligated to either pay for the ensuing long stock position in full (in the case of a call exercised in a cash account or stock subject to 100% margin) or finance the long/short stock position (in the case of a call/put exercised in a margin account). Accounts which do not have sufficient equity on hand prior to exercise introduce undue risk should an adverse price change in the underlying occur upon delivery. This uncollateralized risk can be especially pronounced and may far exceed any in-the-money value the long option may have held, particularly at expiration when clearinghouses automatically exercise options at in-the-money levels as low as $0.01 per share.
Take, for example, an account whose equity on Day 1 consists solely of 20 long $50 strike call options in hypothetical stock XYZ which have closed at expiration at $1 per contract with the underlying at $51. Assume under Scenario 1 that the options are all auto-exercised and XYZ opens at $51 on Day 2. Assume under Scenario 2 that the options are all auto-exercised and XYZ opens at $48 on Day 2.
| Account Balance | Pre-Expiration | Scenario 1 - XYZ Opens @ $51 | Scenario 2 - XYZ Opens @ $48 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $0.00 | ($100,000.00) | ($100,000.00) |
| Long Stock | $0.00 | $102,000.00 | $96,000.00 |
|
Long Option* |
$2,000.00 | $0.00 | $0.00 |
| Net Liquidating Equity/(Deficit) | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | ($4,000.00) |
| Margin Requirement | $0.00 | $25,500.00 | $25,500.00 |
| Margin Excess/(Deficiency) | $0.00 | ($23,500.00) | ($29,500.00) |
*Long option has no loan value.
To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account assuming stock delivery. If the exposure is deemed excessive, IBKR reserves the right to either: 1) liquidate options prior to expiration; 2) allow the options to lapse; and/or 3) allow delivery and liquidate the underlying at any time. In addition, the account may be restricted from opening new positions to prevent an increase in exposure. IBKR determines the number of contracts that will be lapsed by IBKR/auto-exercised shortly after the end of trading on the date of expiration. The effect of any after hours trading you conduct on that day may not be taken into account in this exposure calculation.
While IBKR reserves the right to take these actions, account holders are solely responsible for managing the exercise/assignment risks associated with the positions in their accounts. IBKR is under no obligation to manage such risks for you.
IBKR also reserves the right to liquidate positions on the afternoon before settlement if IBKR’s systems project that the effect of settlement would result in a margin deficit. To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account after settlement. For instance, if IBKR projects that positions will be removed from the account as a result of settlement (e.g., if options will expire out of the money or cash-settled options will expire in the money), IBKR’s systems will evaluate the margin effect of those settlement events.
If IBKR determines the exposure is excessive, IBKR may liquidate positions in the account to resolve the projected margin deficiency. Account holders may monitor this expiration related margin exposure via the Account window located within the TWS. The projected margin excess will be displayed on the line titled “Post-Expiry Margin” (see below) which, if negative and highlighted in red indicates that your account may be subject to forced position liquidations. This exposure calculation is performed 3 days prior to the next expiration and is updated approximately every 15 minutes. Note that certain account types which employ a hierarchy structure (e.g., Separate Trading Limit account) will have this information presented only at the master account level where the computation is aggregated.

Note that IBKR generally initiates expiration related liquidations 2 hours prior to the close, but reserves the right to begin this process sooner or later should conditions warrant. In addition, liquidations are prioritized based upon a number of account-specific criteria including the Net Liquidating Value, projected post-expiration deficit, and the relationship between the option strike price and underlying.
Call Spreads in Advance of Ex-Dividend Date
In the event that you are holding a call spread (long and short calls having the same underlying) prior to an ex-dividend date in the underlying, and if you have not liquidated the spread or exercised the long call(s), IBKR reserves the right to: i) exercise some or all of the long call(s); and/or ii) liquidate (i.e., close out) some or all of the spreads - if IBKR, in its sole discretion, anticipates that: a) the short call(s) is (are) likely to be assigned; and b) your account would not ave sufficient equity to satisfy the liability to pay the dividend or to satisfy margin requirements generally. In the event that IBKR exercises the long call(s) in this scenario and you are not assigned on the short call(s), you could suffer losses. Likewise, if IBKR liquidates some or all of your spread position, you may suffer losses or incur an investment result that was not your objective.
In order to avoid this scenario, you should carefully review your option positions and your account equity prior to any ex-dividend date of the underlying and you should manage your risk and your account accordingly.
Physically Delivered Futures
With the exception of certain futures contracts having currencies or metals as their underlying, IBKR generally does not allow clients to make or receive delivery of the underlying for physically settled futures or futures option contracts. To avoid deliveries in an expiring contract, clients must either roll the contract forward or close the position prior to the Close-Out Deadline specific to that contract (a list of which is provided on the website).
Note that it is the client’s responsibility to be aware of the Close-Out Deadline and physically delivered contracts which are not closed out within the specified time frame may be liquidated by IBKR without prior notification.
Overview of SEC Fees
Under Section 31 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, U.S. national securities exchanges are obligated to pay transaction fees to the SEC based on the volume of securities that are sold on their markets. Exchange rules require their broker-dealer members to pay a share of these fees who, in turn, pass the responsibility of paying the fees to their customers.
This fee is intended to allow the SEC to recover costs associated with its supervision and regulation of the U.S. securities markets and securities professionals. It applies to stocks, options and single stock futures (on a round turn basis); however, IB does not pass on the fee in the case of single stock futures trades. Note that this fee is assessed only to the sale side of security transactions, thereby applying to the grantor of an option (fee based upon the option premium received at time of sale) and the exerciser of a put or call assignee (fee based upon option strike price).
For the fiscal year 2016 the fee was assessed at a rate of $0.0000218 per $1.00 of sales proceeds, however, the rate is subject to annual and,in some cases, mid-year adjustments should realized transaction volume generate fees sufficiently below or in excess of targeted funding levels.1
Examples of the transactions impacted by this fee and sample calculations are outlined in the table below.
|
Transaction |
Subject to Fee? |
Example |
Calculation |
|
Stock Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Stock Sale (cost plus commission option) |
Yes |
Sell 1,000 shares MSFT@ $25.87 |
$0.0000218 * $25.87 * 1,000 = $0.563966 |
|
Call Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Put Purchase |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Call Sale |
Yes |
Sell 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 calls @ $1.17 |
$0.0000218 * $1.17 * 100 * 10 = $0.025506 |
|
Put Sale |
Yes |
Sell 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 puts @ $0.41 |
$0.0000218 * $0.41 * 100 * 10 = $0.008938 |
|
Call Exercise |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Put Exercise |
Yes |
Exercise of 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 puts |
$0.0000218 * $25.00 * 100 * 10 = $0.545 |
|
Call Assignment |
Yes |
Assignment of 10 MSFT June ’11 $25 calls |
$0.0000218 * $25.00 * 100 * 10 = $0.545 |
|
Put Assignment |
No |
N/A |
N/A |
1Information regarding current Section 31 fees may be found on the SEC's Frequently Requested Documents page located at: http://www.sec.gov/divisions/marketreg/mrfreqreq.shtml#feerate
FAQs - U.S. Securities Option Expiration
The following page has been created in attempt to assist traders by providing answers to frequently asked questions related to US security option expiration, exercise, and assignment. Please feel free to contact us if your question is not addressed on this page or to request the addition of a question and answer.
Click on a question in the table of contents to jump to the question in this document.
Table Of Contents:
How do I provide exercise instructions?
Do I have to notify IBKR if I want my long option exercised?
What if I have a long option which I do not want exercised?
What can I do to prevent the assignment of a short option?
Is it possible for a short option which is in-the-money not to be assigned?
What happens if I have a spread position with an in-the-money option and an out-of-the-money option?
Am I charged a commission for exercise or assignments?
Q&A:
How do I provide exercise instructions?
Instructions are to be entered through the TWS Option Exercise window. Procedures for exercising an option using the IBKR Trader Workstation can be found in the TWS User's Guide.
![]() Important Note: In the event that an option exercise cannot be submitted via the TWS, an option exercise request with all pertinent details (including option symbol, account number and exact quantity), should be created in a ticket via the Account Management window. In the Account Management Message Center click on "Compose" followed by "New Ticket". The ticket should include the words "Option Exercise Request" in the subject line. Please provide a contact number and clearly state in your ticket why the TWS Option Exercise window was not available for use.
Important Note: In the event that an option exercise cannot be submitted via the TWS, an option exercise request with all pertinent details (including option symbol, account number and exact quantity), should be created in a ticket via the Account Management window. In the Account Management Message Center click on "Compose" followed by "New Ticket". The ticket should include the words "Option Exercise Request" in the subject line. Please provide a contact number and clearly state in your ticket why the TWS Option Exercise window was not available for use.
Do I have to notify IBKR if I want my long option exercised?
In the case of exchange listed U.S. securities options, the clearinghouse (OCC) will automatically exercise all cash and physically settled options which are in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration (e.g., a call option having a strike price of $25.00 will be automatically exercised if the stock price is $25.01 or more and a put option having a strike price of $25.00 will be automatically exercised if the stock price is $24.99 or less). In accordance with this process, referred to as exercise by exception, account holders are not required to provide IBKR with instructions to exercise any long options which are in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration.
![]() Important Note: in certain situations (e.g., underlying stock halt, corporate action), OCC may elect to remove a particular class of options from the exercise by exception process, thereby requiring the account holder to provide positive notice of their intent to exercise their long option contracts regardless of the extent they may be in-the-money. In these situations, IBKR will make every effort to provide advance notice to the account holder of their obligation to respond, however, account holders purchasing such options on the last day of trading are not likely to be afforded any notice.
Important Note: in certain situations (e.g., underlying stock halt, corporate action), OCC may elect to remove a particular class of options from the exercise by exception process, thereby requiring the account holder to provide positive notice of their intent to exercise their long option contracts regardless of the extent they may be in-the-money. In these situations, IBKR will make every effort to provide advance notice to the account holder of their obligation to respond, however, account holders purchasing such options on the last day of trading are not likely to be afforded any notice.
What if I have a long option which I do not want exercised?
If a long option is not in-the-money by at least $0.01 at expiration it will not be automatically exercised by OCC. If it is in-the-money by at least that amount and you do not wish to have it exercised, you would need to provide IBKR with contrary instructions to let the option lapse. These instructions would need to be entered through the TWS Option Exercise window prior to the deadline as stated on the IBKR website.
What can I do to prevent the assignment of a short option?
The only action one can take to prevent being assigned on a short option position is to buy back in the option prior to the close of trade on its last trading day (for equity options this is usually the Friday preceding the expiration date although there may also be weekly expiring options for certain classes). When you sell an option, you provided the purchaser with the right to exercise which they generally will do if the option is in-the-money at expiration.
Is it possible for a short option which is in-the-money not to be assigned?
While is unlikely that holders of in-the-money long options will elect to let the option lapse without exercising them, certain holders may do so due to transaction costs or risk considerations. In conjunction with its expiration processing, OCC will assign option exercises to short position holders via a random lottery process which, in turn, is applied by brokers to their customer accounts. It is possible through these random processes that short positions in your account be part of those which were not assigned.
What happens if I have a spread position with an in-the-money option and an out-of-the-money option?
Spread positions can have unique expiration risks associated with them. For example, an expiring spread where the long option is in-the-money by less than $0.01 and the short leg is in-the-money more than $0.01 may expire unhedged. Account holders are ultimately responsible for taking action on such positions and responsible for the risks associated with any unhedged spread leg expiring in-the-money.
Can IBKR exercise the out-of-the-money long leg of my spread position only if my in-the-money short leg is assigned?
No. There is no provision for issuing conditional exercise instructions to OCC. OCC determines the assignment of options based upon a random process which is initiated only after the deadline for submitting all exercise instructions has ended. In order to avoid the delivery of a long or short underlying stock position when only the short leg of an option spread is in-the-money at expiration, the account holder would need to either close out that short position or consider exercising an at-the-money long option.
What happens to my long stock position if a short option which is part of a covered write is assigned?
If the short call leg of a covered write position is assigned, the long stock position will be applied to satisfy the stock delivery obligation on the short call. The price at which that long stock position will be closed out is equal to the short call option strike price.
Am I charged a commission for exercise or assignments?
There is no commissions charged as the result of the delivery of a long or short position resulting from option exercise or assignment of a U.S. security option (note that this is not always the case for non-U.S. options).
What happens if I am unable to meet the margin requirement on a stock delivery resulting from an option exercise or assignment?
You should review your positions prior to expiration to determine whether you have adequate equity in your account to exercise your options. You should also determine whether you have adequate equity in the account if an in-the-money short option position is assigned to your account. You should also be aware that short options positions may be exercised against you by the long holder even if the option is out-of-the-money.
If you anticipate that you will be unable to meet the margin requirement on a stock delivery resulting from an option exercise or assignment, you should either close positions or deposit additional funds to your account to meet the anticipated post-delivery margin requirement.
IBKR reserves the right to prohibit the exercise of stock options and/or close short options if the effect of the exercise/assignment would be to place the account in margin deficit. To protect against these scenarios as expiration nears, IBKR will simulate the effect of expiration assuming plausible underlying price scenarios and evaluating the exposure of each account assuming stock delivery. If the exposure is deemed excessive, IBKR reserves the right to either:
- Liquidate options prior to expiration. Please note: While IBKR retains the right to liquidate at any time in such situations, liquidations involving US security positions will typically begin at approximately 9:40 AM ET as of the business day following expiration;
- Allow the options to lapse; and/or
- Allow delivery and liquidate the underlying at any time.
In addition, the account may be restricted from opening new positions to prevent an increase in exposure. IBKR determines the number of contracts that will be lapsed by IBKR/auto-exercised shortly after the end of trading on the date of expiration. The effect of any after hours trading you conduct on that day may not be taken into account in this exposure calculation.
While IBKR reserves the right to take these actions, account holders are solely responsible for managing the exercise/assignment risks associated with the positions in their accounts. IBKR is under no obligation to manage such risks for you.
For more information, please see Expiration & Corporate Action Related Liquidations