如何使用外匯交易者(FX Trader)下單?
TWS可供客戶從外匯交易者(FX Trader)界面創建外匯定單。
儘管外匯交易者界面與定單管理界面有所不同,但交易功能是相同的。
點擊TWS主界面頂部的外匯交易者圖標即可打開外匯交易者,外匯交易者界面以類似“單元格”的形式顯示貨幣對。
![]()
與定單管理界面的市場數據行類似,買價位於左側,賣價位於右側。點擊賣價下買單,點擊買價下賣單。
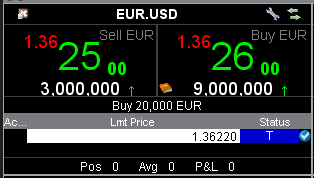
工作中的定單和交易會顯示在外匯交易者窗口第二部分的相應標簽頁中。

注:外匯交易者中創建的定單會顯示在TWS的定單管理界面,但定單管理界面創建的定單無法在外匯交易者窗口查看。
點擊此處觀看有關外匯交易者使用的錄製網研會。
Leveraged FX Currency Restrictions for Israeli Retail Clients
Due to a June 2018 ruling by the Israeli financial court, Interactive Brokers is no longer permitted to offer spot forex trading to Israeli retail clients. While IBKR's forex offering is a deliverable "spot" transaction, the ruling interpreted a 2014 amendment to Israeli Securities Law 5728-1968 to cover spot/cash transactions in addition to derivative/contract style transactions.
- Forex transactions that would create a negative balance or would increase a pre-existing negative balance in either component currency will not be allowed to Israeli retail clients.
- The negative cash balance test applies only to the component currencies and for the cash movements created directly by the forex trade. There is no restriction regarding the creation of negative balances by other means such as cashiering activity or trading activities in securities (stocks, bonds, options, etc).
| Currency | Cash | Cash |
| ILS | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| USD | 1,000 | -2,510 |
| EUR | 0 | 3,000 |
USD -2,000.
| Currency | Cash | Stock | Cash | Stock |
| USD | 1,000 | 0 | -2,000 | 3,000 |
Example: Having USD 1,000 and converting to ILD, value of ILS 3,600 (1 USD = 3.6 ILS)
|
Currency
|
Cash
|
Cash
|
|
ILS
|
0
|
3,600
|
|
USD
|
1,000
|
0
|
|
Currency
|
Cash
|
Cash
|
|
EUR
|
0
|
-600
|
|
USD
|
1,000
|
1,000
|
Procedure
In order to be consider a "Qualified Investor" IB requires client to meet the following criteria and procedural requirements.
Qualified Investor qualification need to be recertified every 3 years.
For Individuals
Individuals, which comply with at least one of the following alternatives:
- Total value of Liquid Assets greater than NIS 8 million; or
- Annual income in each preceding two years is greater than NIS 1.2 million or the income of the Household to which he belongs is greater than NIS 1.8 million.; or
- Total value of Liquid Assets greater than NIS 5 million and the annual income in each proceeding two years is greater than NIS 600,000 or such annual income of the Household to which he belongs is greater than NIS 900,000.
"Liquid Assets" means cash, deposits, securities, equities and funds.
"Household" means an individual and the persons living with him or who are dependent on him for their living.
The client must:
- compete the Qualified Investor Representation form and
- provide a written signed confirmation from a registered attorney or accountant certifying their qualification. This certification should be no older than 3 months.
For Corporates
The following entities can be exempted:
- Authorized mutual funds or fund managers
- Provident funds or fund managers
- Insurers
- Banking corporations
- Portfolio managers
- Investment advisors, who acquire for themselves
- Stock Exchange members
- Underwrites, who buy for themselves
- Venture capital funds
- Corporations (including funds, partnerships) other than corporations which were incorporated for the purpose of purchasing securities in a specific offer, with equity exceeding 50 million NIS
- Corporations, wholly owned by one of the aforementioned investors
Entities qualifying under exemptions 1-9 must provide confirmation of their status from a governmental register.
Entities that wish to be considered under exemptions 10 and 11 must:
- complete the Qualified Investor Representation form and
- provide a written signed confirmation from a registered attorney or accountant certifying their qualification. This certification should be no older than 3 months.
Forex Execution Statistics
IBKR clients can now analyze the quality of their forex executions in comparison to forex trades by other IBKR customers through the FX Browser tool in Client Portal. The tool provides transaction data for the 15 forex transactions that occur immediately before and after in the same currency pair of the client's transaction.
Note:
The number of transactions may be limited to fewer than the stated 15 as the NFA also has placed a 15 minute window on the query. Meaning, if within a 15 minute window before and after the customer's execution there are fewer than 15 executions the customer's query will return only those executions which occurred within the time window.
Accessing the FX Browser Tool
To Access the FX Browser tool, login to Client Portal using the Login button on our website. Click the Help menu (question mark icon in the top right corner) followed by Support Center. Please note, at this time only data for the live account will be provided.
.png)
From there, select "See Trades on IBKR's FX Platform" from the list of Information & Tools:

Submitting a Query
When the FX Browser is launched, you will be presented with the following screen:
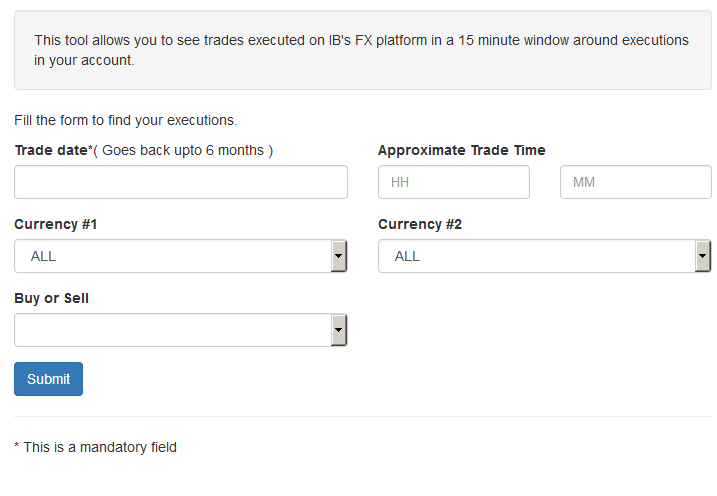
Please note that only Trade Date is a mandatory field in the query. When clicking on the Trade Date field, a calendar widget will populate and allow you to select your trade date. Only transactions from the last 6 months will be available to search.
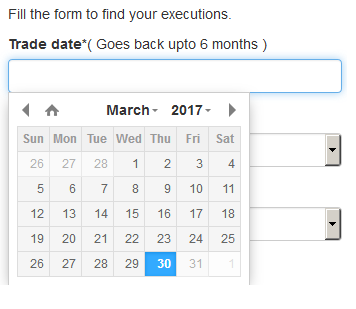
Active customers may wish to limit the results by further selecting the currency pair, side or time of the execution.
Once the desired query has been entered, click on the Submit button.
The next screen will display the list of executions for the given account on the specified day. From there, you may select the execution you wish to receive the execution statistics on.
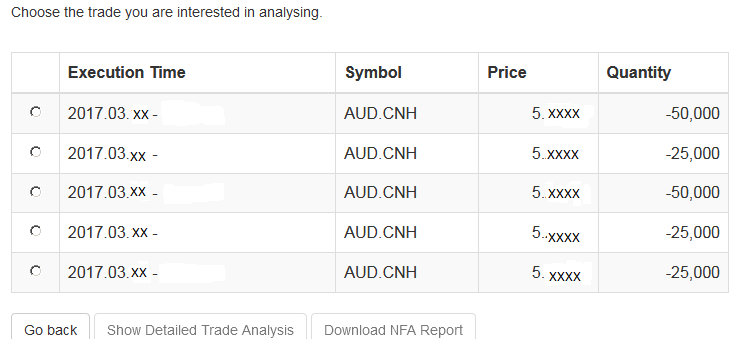
Once the execution you wish to view has been selected, click the "Download NFA Report" button.

Reading the Report
The results will be returned in a new tab and will contain the 15 executions before and 15 executions after the trade you selected on the previous screen. Per the note above, if fewer than 15 executions occurred in the 15 minute time frame only those executions will be displayed.
The query results will include the following information:
- Execution date and time, as expressed in Eastern time
- Side (buy or sell)
- Quantity (of Transaction Currency)
- Currency pair
- Execution price
- Commissions and other charges assessed by the FDM
- Currency denomination of commissions
Your trade will be marked as Trade Number "0" and the trades before and after your trade will be numbered from 1 to 15.
Error Messages
If the search criteria you enter does not bring up any trade information, you will be presented with the following error message:
Automatic Forex Swap
OVERVIEW
In general, interest on account balances are credited/debited at benchmark rates plus/minus a spread as shown on our web pages. For qualified clients with substantial forex positions, however, IB has created a mechanism to carry large gross FX positions with higher efficiency with respect to carrying costs. We refer to it as the “auto swap program”. The design allows clients to benefit from IB’s participation in the interbank forex swaps market where implied interest rate spreads are usually much narrower than the spreads available in the retail deposit market.
a. Concept
Interest is charged on settled balances, so the intent of a Forex swap as used here is to defer the settlement of a currency position from one day to the next business day. This is done by a simultaneous sell and buy of the same amount of base (first) currency but for two different value dates e.g. on T you go long 10 mio. EUR.USD for value date T+2. By example, on T+1 the position is swapped T+2 to T+3, here a sell of 10 mio EUR.USD for T+2 and a purchase of 10 mio. EUR.USD for T+3. As a result you have deferred settlement from T+2 to T+3, with the difference in prices of the two trades representing the financing cost from T+2 to T+3.
b. Cost
This service is provided as a free service and no commission or markup is charged by Interactive Brokers. The interbank market bid/ask spread inherent in the swap prices may be regarded as a cost but is not determined by Interactive Brokers. Interactive Brokers provides the service on a best efforts basis to our large Forex clients.
c. Position Criteria
Swap activity is only applied to accounts with gross FX positions larger than 10 mio. USD or approximate equivalent of other currencies. Positions are swapped (rolled) in increments or multiples of USD 1 mio. (or equivalent). The residual settled balances are traded under IB‘s standard interest model1. Positions that are swapped (rolled) are real positions, i.e. the projected T+1 settled cash balances.
The so-called “Virtual Positions” are not considered; the virtual position is only a representation of the original trades expressed as currency pairs, for example EUR.CHF.
Settled cash balances are a single currency concept, e.g. EUR or CNH. IB executes all swaps against USD as it is the most efficient funding currency. Should you have a position in a cross, e.g. EUR against CHF, two swaps, one in EUR.USD and one in USD.CHF will be done. The threshold(s) and increment(s) may change at any time without notice.
d. Client Eligibility
As we offer this service for free, only clients with substantial currency positions are eligible for inclusion in the service. US legal residents need to be an Eligible Contract Participant (ECP) and be in the possession of an LEI number (legal entity identifier). Interactive Brokers cannot guarantee a client’s inclusion in the program and all inquiries require compliance approval prior to become active.2
e. Swap Price Recognition
Interactive Brokers may conduct a series of swaps in a currency during a day. Interactive Brokers will use average bid and ask prices at which it executed, respectively average bid and asks as quoted in the interbank market. Swap prices are not published but can be seen (or calculated) in the statement after execution. The swaps are applied in the account at the end of the day.
f. Recognition in the Statement
You will find the swap transaction(s) in the Trades section of the statement. The swap are represented as simultaneous purchase/sale or vice versa, do not have a time stamp and shows an M (manual entry) in the code column. The actual swap prices are the difference in between the two prices.
Here an example for cob 20150203 that shows a swap from 20150203 to 20150204.
![]()
.jpg)
g. Examples of Swap Prices
Here a couple of examples that use swap prices from a major interbank provider. Often bid/ask spreads are even tighter.
|
Currency Pair |
Spot Bid |
Spot Ask |
Tenor |
Days in Period (TN) |
Swap Points Bid |
Swap Points Ask |
Implied Currency |
Implied Rate Bid |
Implied Rate Ask |
|
EUR.USD |
1.04481 |
1.04483 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.00004220 |
0.00004280 |
EUR |
-0.77% |
-0.75% |
|
USD.HKD |
7.76810 |
7.76810 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.00011500 |
-0.00011000 |
HKD |
0.17% |
0.19% |
|
USD.JPY |
117.050 |
117.052 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
-0.0038 |
-0.0032 |
JPY |
-0.47% |
-0.47% |
|
USD.CNH |
6.93101 |
6.93105 |
TomNext(TN) |
1 |
0.0021 |
0.0028 |
CNH |
11.77% |
15.46% |
In more detail, let’s assume you want to calculate the implied CNH rate resulting from a USD.CNH swap. We are looking for the implied rate of the quote currency CNH (Currency 2). Therefore the following formula is used:
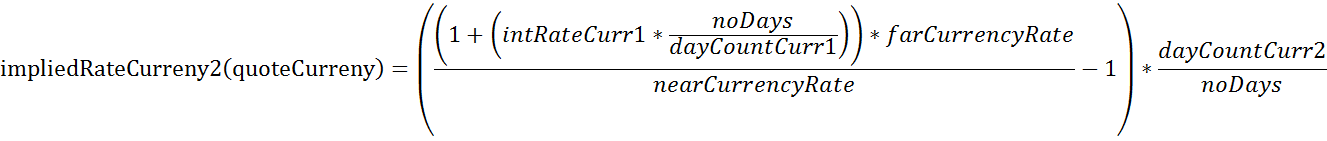
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | USD.CNH | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. CNH | dayCountCurr2 | 365 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 1 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr1 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 6.939500 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.0012 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 6.938300 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 6.939500 |
| implied interes rate of Currency2, i.e. CNH | impliedRateCurrncy2(quoteCurrency) | 0.0702 |
So using above figures, this results in a 7.02% implied interest rate for CNH.
Now if you wanted to calculate the implied rate for the base currency (Currency 1) the formula would change slightly. Here an example using EUR.USD:
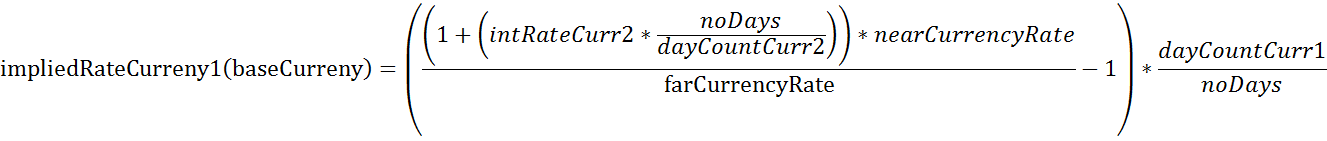
| Description | Variable | Value |
| Currency Pair (Currency1.Currency2) | EUR.USD | |
| day count convention Currency 1 (base Currency), i.e. EUR | dayCountCurr1 | 360 |
| day count convention Currency 2 (quote Currency), i.e. USD | dayCountCurr2 | 360 |
| Tenor | TomNext | |
| number of days in the Tenor | noDays | 1 |
| interest rate of Currency 2 (in decimals, i.e. 1% = 0.01) | inRateCurr2 | 0.0070 |
| Currency rate (Spot) | currencyRate | 1.039900 |
| swap Points expressed in decimals | swapPoints | 0.000042 |
| near Currency Rate (Spot - swap points) | nearCurrencyRate | 1.039858 |
| far Currency Rate (in a Tomnext swap this is the spot rate) | farCurrencyRate | 1.039900 |
| implied interes rate of Currency1, i.e. EUR | impliedRateCurrncy1(baseCurrency) | -0.0075 |
Using above example, this results in a -0.75 % implied interest rate for EUR.
1. For example, in the case of a USD 20.3 mio. position only 20 mio. will be swapped. USD 0.3 remains in the account and interest using benchmark and spreads will be applied. A USD 300k position will not be considered for swapping at all. The position by currency is taken as the reference, regardless of the overall position.
2 US, Australian and Israeli domiciled residents are currently not eligible for inclusion in the Automated Forex Swap Program.
Summary of Risks relating to Forex CFDs issued by Interactive Brokers Securities Japan, Inc.
This summary highlights the principal risks associated with trading Forex CFDs issued by IBSJ (“IB FXCFDs"). It is not a risk disclosure for regulatory purposes.
- Trading of IB FXCFDs is not suitable for all investors, and you should not trade them unless you are an experienced investor with a high risk tolerance and the capability to sustain losses if they occur
- The volatility of foreign exchange rates and interest rates may quickly cause significant losses. Forex CFDs employ leverage that further amplifies the volatility relative to your investment and you may lose more than you have invested. In addition, IB FXCFD roll over interest may turn from a credit to a debit due to changes in interest rates
- You are required to maintain sufficient equity in your account at all times to cover IBSJs maintenance margin requirement. There are no grace-periods and IBSJ does not issue margin calls. Your equity is calculated in real time and should it become insufficient, IBSJ will immediately and automatically liquidate positions to bring your account into margin compliance. Real time liquidations aim to minimize the risk that your account equity becomes negative, but they cannot eliminate that risk. Should your equity become negative you are required to deposit additional funds to cover the deficit
- The price IBSJ displays to you for IB FXCFDs is based on the prevailing foreign exchange market. However there is no guarantee for executions at that price. Slippage may occur for large trades or in fast moving markets and during heavily traded hours
- Moreover, your ability to establish or close positions on a timely basis is not guaranteed. It may become difficult to display quotes during major holidays or during hours when foreign exchange trading is not active. IBSJ may display prices that deviate from a fair market due to system-malfunctions or failures, or erroneous quotes that IBSJ may receive from market participants or for other reasons (off-market prices). IBSJ will adjust or cancel trades executed with off-market prices
- IB FXCFDs are over-the-counter trades between you and IBSJ. They are not traded on any exchange or cleared by any central counterparty. You are therefore exposed to counterparty risk and should IBSJ become insolvent you may not be able to fully recoup your investment, or at all
Please contact IBSJs Client Service Department should you have questions about the content of this summary and read the full risk disclosure carefully before commencing trading. The risk disclosure is available in Account Management when you request IB FXCFD trading permissions, and on IBSJs web site.
IB外匯差價合約 - 事實與常見問題
風險警告
差價合約屬於復雜金融產品,其交易存在高風險,由於杠杆的作用,可能會出現迅速虧損。
在通過IBKR(UK)交易差價合約時,有67%的零售投資者賬戶出現了虧損。
您應考慮自己是否理解差價合約的運作機制以及自己是否能夠承受虧損風險。
ESMA差價合約規定(僅限零售客戶)
歐洲證券與市場管理局(ESMA)頒布了新的差價合約規定,自2018年8月1日起生效。
新規包括:1) 開倉差價合約頭寸的杠杆限制;2) 以單個賬戶為單位的保證金平倉規則;以及3) 以單個賬戶為單位的負余額保護規則;ESMA規定僅適用於零售客戶。
專業客戶不受影響。
請參見ESMA差價合約新規推行了解更多詳細信息。
IBKR外匯差價合約特點
透明的直接市場接入(DMA)報價:IB收緊的點差與丰富的流動性源於14家全球最大外匯交易商的聯合報價,這些交易商占有全球銀行衕業拆借市場的份額超過70%*。因此顯示的報價低至0.1個點差(PIP)。IB不會標高報價,而是會將其接收到的價格直接傳遞給客戶并單獨收取低廉的佣金。
*來源:歐洲貨幣雜志外匯調查(Euromoney FX survey)外匯投票2016。
例如,2016年4月21日,英鎊基准利率為0.483%,美元基准利率為0.37%。則適用的基准利率為:
GBP.USD基准 +0.483% - 0.37% = +0.113%
適用的客戶利率為貨幣對基准 – IB多頭頭寸點差,基准 + 空頭頭寸點差:
GBP.USD多頭利率 +0.113% - 1.00% = -0.887%
GBP.USD空頭利率 +0.113% + 1.00% = +1.113%
請注意,多頭利率為貸項,空頭利率為借項。因此,對於多頭頭寸,正利率意味著您會收到利息,負利率意味著您會被收取利息。而對於空頭頭寸,正利率意味著您會被收取利息,負利率意味著您會收到利息。
利率根據以報價貨幣表示的合約價值進行計算,并以該貨幣收取或支付利息。舉例:
舉例:
| 每日利息 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 頭寸 | GBP.USD收槃價 | USD價值 | 利率 | USD | |
| GBP.USD | -20,000 | 1.43232 | -28,646.40 | 1.113% | -0.89 |
外匯差價合約余額利息基於合約單獨計算,而不是與其他貨幣頭寸(包括即期外匯)合并或總括計算。盡管IB不會直接引用互換利率,但IB保留在特殊市場條件下(如財年結束前后的互換利率迅速上升)應用較高點差的權利。
交易舉例(專業客戶)
開倉
您以$1.16195的價格買入10手(200000)EUR.CHF差價合約,總計CHF 232,390,持有5天。
| EUR.CHF外匯差價合約 – 新頭寸 | |
|---|---|
| 參考底層證券價格 | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| 差價合約參考價格 | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| 行動 | 買入 |
| 數量 | 200,000 |
| 交易價值 | CHF 232,390.00 |
| 保證金(3% x 232,390) | AUD 9,100 |
| 收取的利息(232,390瑞郎5天的利息) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 第一階梯(貨幣對BM 0.42% - IB點差1%) | CHF 232,390.00 | -0.58% | (CHF 18.72) |
平倉
| 平倉差價合約頭寸 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 盈利情境 | 虧損情境 | |
| 參考底層證券價格 | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| 差價合約參考價格 | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| 行動 | 賣出 | 賣出 |
| 數量 | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| 交易價值 | CHF 233,680.00 | CHF 231,078.00 |
| 交易盈虧 | CHF 1,290.00 | (CHF 1,312.00) |
| 融資 | (CHF 18.72) | (CHF 18.72) |
| 開倉佣金0.002% | (CHF 4.65) | (CHF 4.65) |
| 開倉佣金0.002% | (CHF 4.67) | (CHF 4.62) |
| 總盈虧 | CHF 1,261.96 | (CHF 1,339.99) |
差價合約的相關資源
下方鏈接可幫助您了解更多有關IB差價合約產品的詳細信息:
常見問題
任何人都能交易IB外匯差價合約嗎?
除美國、加拿大和香港的居民,其他所有客戶都能交易IB差價合約。任何投資者類型都不能免於這一基於居住地的限制。
IB外匯差價合約和IB現金外匯之間的區別是什么?
IB現金外匯是一種帶杠杆的現金交易,可實物交割貨幣對的兩種貨幣。您的外匯交易相關余額會與您其他交易活動產生的其他余額合并,且您需根據每種貨幣的基准利率為這些合并余額支付利息或收取相關利息。
相比之下,IB外匯差價合約是一種提供倉位但不支持實物交割底層貨幣的合約,且您是根據合約的名義價值支付或收取利息的。合約的基准利率是兩種底層貨幣的基准利率差額。這基本上與其他經紀商使用的隔夜利息(TOM Next)展期相似,但由於基准利率的波動性通常小於互換利率,該息差的穩定性更高。
請參見上方的息差部分查看詳細舉例。
有什么市場數據要求嗎?
IB外匯差價合約的市場數據與杠杆外匯相衕。其為全局許可且免費。
差價合約交易與頭寸在報表中如何反映?
如果您在IB LLC持有賬戶,且您的差價合約頭寸持有在單獨的賬戶段(主賬戶號碼加后綴“F”)中。您可選擇單獨查看F賬戶段的活動報表,也可以選擇與主賬戶合并查看。您可在賬戶管理的報表窗口進行選擇。
我可以釆用與即期外匯一樣的定單類型和算法交易外匯差價合約嗎?我可以在外匯交易者中進行這種交易嗎?
可以,交易是一樣的。
Allocation of Partial Fills
How are executions allocated when an order receives a partial fill because an insufficient quantity is available to complete the allocation of shares/contracts to sub-accounts?
Overview:
From time-to-time, one may experience an allocation order which is partially executed and is canceled prior to being completed (i.e. market closes, contract expires, halts due to news, prices move in an unfavorable direction, etc.). In such cases, IB determines which customers (who were originally included in the order group and/or profile) will receive the executed shares/contracts. The methodology used by IB to impartially determine who receives the shares/contacts in the event of a partial fill is described in this article.
Background:
Before placing an order CTAs and FAs are given the ability to predetermine the method by which an execution is to be allocated amongst client accounts. They can do so by first creating a group (i.e. ratio/percentage) or profile (i.e. specific amount) wherein a distinct number of shares/contracts are specified per client account (i.e. pre-trade allocation). These amounts can be prearranged based on certain account values including the clients’ Net Liquidation Total, Available Equity, etc., or indicated prior to the order execution using Ratios, Percentages, etc. Each group and/or profile is generally created with the assumption that the order will be executed in full. However, as we will see, this is not always the case. Therefore, we are providing examples that describe and demonstrate the process used to allocate partial executions with pre-defined groups and/or profiles and how the allocations are determined.
Here is the list of allocation methods with brief descriptions about how they work.
· AvailableEquity
Use sub account’ available equality value as ratio.
· NetLiq
Use subaccount’ net liquidation value as ratio
· EqualQuantity
Same ratio for each account
· PctChange1:Portion of the allocation logic is in Trader Workstation (the initial calculation of the desired quantities per account).
· Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user
· Inline Profile
The ratio is prescribed by the user.
· Model1:
Roughly speaking, we use each account NLV in the model as the desired ratio. It is possible to dynamically add (invest) or remove (divest) accounts to/from a model, which can change allocation of the existing orders.
Basic Examples:
Details:
CTA/FA has 3-clients with a predefined profile titled “XYZ commodities” for orders of 50 contracts which (upon execution) are allocated as follows:
Account (A) = 25 contracts
Account (B) = 15 contracts
Account (C) = 10 contracts
Example #1:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 10 am (ET) the order begins to execute2but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 2 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 7 of the 50 contracts are filled or 14%). For each account the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 14% of 25 = 3.5 rounded down to 3
Account (B) = 14% of 15 = 2.1 rounded down to 2
Account (C) = 14% of 10 = 1.4 rounded down to 1
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.10).
A: final allocation of 3 contracts, which is 3/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.12)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 2 contract, which is 2/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.20)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #2:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be filled3 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 1 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is executed (i.e., 5 of the 50 contracts are filled or 10%).For each account, the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers:
Account (A) = 10% of 25 = 2.5 rounded down to 2
Account (B) = 10% of 15 = 1.5 rounded down to 1
Account (C) = 10% of 10 = 1 (no rounding necessary)
To Summarize:
A: initially receives 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The system then allocates the next (and final) contract to an account with the smallest ratio (i.e. to Account B which currently has a ratio of 0.067).
A: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.08)
B: final allocation of 2 contracts, which is 2/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.134)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Example #3:
CTA/FA creates a DAY order to buy 50 Sept 2016 XYZ future contracts and specifies “XYZ commodities” as the predefined allocation profile. Upon transmission at 11 am (ET) the order begins to be executed2 but in very small portions and over a very long period of time. At 12 pm (ET) the order is canceled prior to being executed in full. As a result, only a portion of the order is filled (i.e., 3 of the 50 contracts are filled or 6%). Normally the system initially allocates by rounding fractional amounts down to whole numbers, however for a fill size of less than 4 shares/contracts, IB first allocates based on the following random allocation methodology.
In this case, since the fill size is 3, we skip the rounding fractional amounts down.
For the first share/contract, all A, B and C have the same initial fill ratio and fill quantity, so we randomly pick an account and allocate this share/contract. The system randomly chose account A for allocation of the first share/contract.
To Summarize3:
A: initially receives 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
C: initially receives 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
Next, the system will perform a random allocation amongst the remaining accounts (in this case accounts B & C, each with an equal probability) to determine who will receive the next share/contract.
The system randomly chose account B for allocation of the second share/contract.
A: 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: 0 contracts, which is 0/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.00)
The system then allocates the final [3] share/contract to an account(s) with the smallest ratio (i.e. Account C which currently has a ratio of 0.00).
A: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/25 of desired (fill ratio = 0.04)
B: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/15 of desired (fill ratio = 0.067)
C: final allocation of 1 contract, which is 1/10 of desired (fill ratio = 0.10)
The execution(s) received have now been allocated in full.
Available allocation Flags
Besides the allocation methods above, user can choose the following flags, which also influence the allocation:
· Strict per-account allocation.
For the initially submitted order if one or more subaccounts are rejected by the credit checking, we reject the whole order.
· “Close positions first”1.This is the default handling mode for all orders which close a position (whether or not they are also opening position on the other side or not). The calculation are slightly different and ensure that we do not start opening position for one account if another account still has a position to close, except in few more complex cases.
Other factor affects allocations:
1) Mutual Fund: the allocation has two steps. The first execution report is received before market open. We allocate based onMonetaryValue for buy order and MonetaryValueShares for sell order. Later, when second execution report which has the NetAssetValue comes, we do the final allocation based on first allocation report.
2) Allocate in Lot Size: if a user chooses (thru account config) to prefer whole-lot allocations for stocks, the calculations are more complex and will be described in the next version of this document.
3) Combo allocation1: we allocate combo trades as a unit, resulting in slightly different calculations.
4) Long/short split1: applied to orders for stocks, warrants or structured products. When allocating long sell orders, we only allocate to accounts which have long position: resulting in calculations being more complex.
5) For non-guaranteed smart combo: we do allocation by each leg instead of combo.
6) In case of trade bust or correction1: the allocations are adjusted using more complex logic.
7) Account exclusion1: Some subaccounts could be excluded from allocation for the following reasons, no trading permission, employee restriction, broker restriction, RejectIfOpening, prop account restrictions, dynamic size violation, MoneyMarketRules restriction for mutual fund. We do not allocate to excluded accountsand we cancel the order after other accounts are filled. In case of partial restriction (e.g. account is permitted to close but not to open, or account has enough excess liquidity only for a portion of the desired position).
Footnotes:
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Stop Orders
U.S. equity markets occasionally experience periods of extraordinary volatility and price dislocation. Sometimes these occurrences are prolonged and at other times they are of very short duration. Stop orders may play a role in contributing to downward price pressure and market volatility and may result in executions at prices very far from the trigger price.
IB Forex CFDs - Facts and Q&A
Risk Warning
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
ESMA Rules for CFDs (Retail Clients only)
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has enacted new CFD rules effective 1st August 2018.
The rules include: 1) leverage limits on the opening of a CFD position; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; and 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis. The ESMA Decision is only applicable to retail clients.
Professional clients are unaffected.
Please refer to the following articles for more detail:
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) and IBKR LLC
ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBIE and IBCE
IBKR Forex CFD Features
Transparent DMA Quotes: IBKR ensures tight spreads and substantial liquidity as a result of combining quotation streams from 14 of the world's largest foreign exchange dealers which constitute more than 70% of market share in the global interbank market*. This results in displayed quotes as small as 0.1 PIP. IBKR does not mark up the quotes, rather passes through the prices that it receives and charges a separate low commission.
*Source: Euromoney FX survey FX Poll 2016.
For example, April 21, 2016 the GBP benchmark rate was 0.483%, the USD rate was 0.37%. The applicable benchmark rate is:
GBP.USD BM +0.48% - 0.37% = +0.113%
The applicable customer rate is Pair BM – IBKR spread for long positions, BM + spread for short positions:
GBP.USD Long Rate +0.113% - 1.00% = -0.887%
GBP.USD Short Rate +0.113% + 1.00% = +1.113%
It is important to note that the long rate is applied as a credit, the short rate as a debit. Consequently for a long position a positive rate means a credit, a negative rate a charge. However for short positions a positive rate means a charge, a negative rate a credit.
Interest is calculated on the contract value expressed in the quote currency, and credited or debited in that currency. For example:
For example:
| Daily Interest | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | GBP.USD Close | USD Value | Rate | USD | |
| GBP.USD | -20,000 | 1.43232 | -28,646.40 | 1.113% | -0.89 |
Interest on Forex CFD balances is calculated on a stand-alone contract basis, and not combined or netted with other currency exposures, including Spot FX. Although IBKR does not directly reference swap rates, IBKR reserves the right to apply higher spreads in exceptional market conditions, such as during spikes in swap rates that can occur around fiscal year-ends.
If your account is with IBKR (UK) or with IBKR LLC, IBKR will then set up a new account segment (identified with your existing account number plus the suffix “F”). Once the set-up is confirmed you can begin to trade. You do not need to fund the F-account separately, funds will be automatically transferred to meet CFD margin requirements from your main account.
If your account is with another IBKR entity, only the permission is required; an additional account segment is not necessary.
Trading Example (Professional Clients)
Opening the position
You purchase 10 lots (200000) EUR.CHF CFDs at $1.16195 for CHF 232,390, which you then hold for 5 days.
| EUR.CHF Forex CFDs – New Position | |
|---|---|
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| Action | Buy |
| Quantity | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 232,390.00 |
| Margin (3% x 232,390) | AUD 9,100 |
| Interest Charged (on CHF 232,390 over 5 days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I (Pair BM 0.42% - IB Spread 1%) | CHF 232,390.00 | -0.58% | (CHF 18.72) |
Closing the position
| Exit CFD Position | ||
|---|---|---|
| Profit Scenario | Loss Scenario | |
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| Action | Sell | Sell |
| Quantity | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 233,680.00 | CHF 231,078.00 |
| Trade P&L | CHF 1,290.00 | (CHF 1,312.00) |
| Financing | (CHF 18.72) | (CHF 18.72) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.65) | (CHF 4.65) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.67) | (CHF 4.62) |
| Total P&L | CHF 1,261.96 | (CHF 1,339.99) |
CFD Resources
Below are some useful links with more detailed information on IBKR’s CFD offering:
Frequently Asked Questions
Can anyone trade IBKR Forex CFDs?
All clients can trade IBKR CFDs, except residents of the USA, Canada, and Hong Kong. There are no exemptions based on investor type to the residency-based exclusions.
What is the difference between IBKR Forex CFDs and IBKR Cash Forex?
IBKR Cash Forex is a leveraged cash trade where you take delivery of the two currencies making up the pair. Your Forex-trading related balances are combined with your other balances arising out of your other trading activity, and you pay or receive interest on these consolidated balances based on the benchmark rate for each currency.
By contrast IBKR Forex CFDs are a contract which provides exposure but does not deliver the underlying currencies, and you pay or receive interest on the notional value of the contract. The benchmark rate for the contract is the difference between the benchmark rates for the two underlying currencies. This is in principle similar to the TOM Next rolls used by other brokers, but offers greater stability as benchmark rates generally are less volatile than swap rates.
Please see the Carry Interest section above for a detailed example.
Are there any market data requirements?
The market data for IBKR Forex CFDs is the same as for Leverage FX. It is a global permission and free of charge.
How are my CFD trades and positions reflected in my statements?
If you are a client of IBKR (U.K.) or IBKR LLC, your CFD positions are held in a separate account segment identified by your primary account number with the suffix “F”. You can choose to view Activity Statements for the F-segment either separately or consolidated with your main account. You can make the choice in the statement window in Client Portal.
If you are a client of other IBKR entities, there is no separate segment. You can view your positions normally alongside your non-CFD positions.
Can I trade Forex CFDs with the same order types and algos as Spot FX, and can I trade them in the FX Trader?
Yes, the trading experience is identical.
盈透證券歡迎您
現在您的賬戶已完成入金并獲批,您可以開始交易了。以下信息可以幫助您入門。
- 您的資金
- 設置您的賬戶以進行交易
- 如何交易
- 在全球範圍進行交易
- 拓展您IB經驗的五個要點
1. 您的資金
存款&取款基本信息。所有轉賬都通過您的賬戶管理進行管理
存款
首先,通過您的賬戶管理 > 資金 > 資金轉賬 > 轉賬類型:“存款”創建一個存款通知(如何創建存款通知)。第二步,通知您的銀行進行電匯轉賬,在存款通知中提供詳細銀行信息。
取款
通過您的賬戶管理 > 資金 > 資金轉賬 > 轉賬類型:“取款”創建一個取款指令(如何創建取款指令)
如果您通知要進行超出取款限額的取款,則會被視為異常取款,我們因此將需要匹配銀行賬戶持有人和IB賬戶。如果目的地銀行賬戶已被用作存款,那麼取款將會被處理;否則,您必須聯繫客戶服務并提供所需文件。
錯誤排查
存款:我的銀行發出了資金,但我沒有看到資金記入我的IB賬戶。可能的原因:
a) 資金轉賬需要1至4個工作日。
b) 存款通知缺失。您必須通過賬戶管理創建存款通知并向客戶服務發送一條咨詢單。
c) 修改詳情缺失。轉賬詳情中缺失您的姓名和IB賬戶號碼。您必須聯繫您的銀行索取完整的修改詳情。
d) IB發起的ACH存款7個工作日內限額為10萬美元。如果您開立的是初始要求為11萬美元的投資組合保證金賬戶,最好選擇電匯存款以減少您第一筆交易的等待時間。如果選擇ACH,會需要等待近2周時間,或者可以選擇臨時升級至RegT。
取款:我已經請求了取款,但我沒有看到資金記入我的銀行賬戶。可能的原因:
a) 資金轉賬需要1至4個工作日。
b) 被拒。超出最大取款限額。請檢查您賬戶的現金餘額。注意,出於監管要求,存入資金時會有三天置存期,之後才可以被取出。
c) 您的銀行退回了資金。可能是因為接收銀行賬戶與匯款銀行賬戶名稱不匹配。
2. 設置您的賬戶以進行交易
現金與保證金賬戶的區別:如果您選擇快速申請,默認您的賬戶類型為配備美國股票許可的現金賬戶。如果您想使用槓桿并以保證金交易,參見此處如何升級為RegT保證金賬戶
交易許可
為了能夠交易特定國家的某一特定資產類別,您需要通過賬戶管理獲得該資產類別的交易許可。請注意,交易許可是免費的。但您可能需要簽署當地監管部門所要求的風險披露。如何請求交易許可
市場數據
如果想獲取某一特定產品/交易所的實時市場數據,您需要訂閱交易所收費的市場數據包。如何訂閱市場數據
市場數據助手會幫助您選擇正確的數據包。請觀看該視頻,其解釋了市場數據助手是如何工作的。
客戶可以通過從未訂閱的代碼行點擊免費延時數據按鈕選擇接收免費的延時市場數據。
顧問賬戶
請閱讀用戶指南顧問入門指南。在這裡,您可以看到如何向您的顧問賬戶創建其他使用者以及如何授予其訪問權限等等。
3. 如何交易
如果想學習如何使用我們的交易平台,您可以訪問交易者大學。在這裡您可以找到我們以10種語言提供的實時與錄製網研會以及有關交易平台的課程與文檔。
交易者工作站(TWS)
要求更高級交易工具的交易者可以使用我們做市商設計的交易者工作站(TWS)。TWS有著便於操作的電子表格式界面,可優化您的交易速度和效率,支持60多種定單類型,配備可適應任何交易風格的特定任務交易工具,并可實時監控賬戶餘額與活動。試試兩種不同模式:
魔方TWS:直觀可用性, 簡便的交易准入,定單管理,自選列表與圖表全部在一個窗口呈現。
標準模式TWS:為需要更高級工具與算法的交易者提供高級定單管理。
基本描述與信息 / 快速入門指南 / 用戶指南
互動課程:TWS基礎 / TWS設置 / 魔方TWS
如何下單交易:標準模式TWS視頻 / 魔方TWS視頻
交易工具:基本描述與信息 / 用戶指南
要求:如何安裝適用於Windows的Java / 如何安裝適用於MAC的Java / 需打開端口4000和4001
登錄TWS / 下載TWS
網絡交易者(WebTrader)
偏好乾淨簡潔界面的交易者可以使用我們基於HTML的網絡交易者。網絡交易者便於查看市場數據、提交定單以及監控您的賬戶與執行。從各瀏覽器使用最新版本網絡交易者
快速入門指南 / 網絡交易者用戶指南
簡介:網絡交易者視頻
如何下單交易:網絡交易者視頻
登錄網絡交易者
移動交易者(MobileTrader)
我們的移動解決方案可供您隨時隨地用您的IB賬戶進行交易。IB TWS iOS版和IB TWS BlackBerry版是為這些型號定制設計的,而通用的移動交易者支持大多數其他職能手機。
基本描述與信息
定單類型 可用定單類型與描述 / 視頻 / 課程 / 用戶指南
模擬交易 基本描述與信息 / 如何獲得模擬交易賬戶
一旦您的模擬交易賬戶創建成功,您便可用模擬交易賬戶分享您真實賬戶的市場數據:賬戶管理 > 管理賬戶 > 設置 > 模擬交易
4. 在全球範圍進行交易
IB賬戶為多幣種賬戶。您的賬戶可以同時持有不同的貨幣,可供您從一個賬戶交易全球範圍內的多種產品。
基礎貨幣
您的基礎貨幣決定了您報表的轉換貨幣以及用於確定保證金要求的貨幣。基礎貨幣在您開立賬戶時決定。客戶隨時可通過賬戶管理改變其基礎貨幣。
我們不會自動將貨幣轉換為您的基礎貨幣
貨幣轉換必須由客戶手動完成。在該視頻中,您可以學習如何進行貨幣轉換。
要開倉以您賬戶所不持有之貨幣計價的頭寸,您可以有以下兩種選擇:
A) 貨幣轉換。
B) IB保證金貸款。(對現金賬戶不可用)
請查看該課程,其解釋了外匯交易方法。
5. 拓展您IB經驗的五個要點
1. 合約搜索
在這裡,您會找到我們的所有產品、代碼與說明。
2. IB知識庫
IB知識庫包含了一系列術語、指導性文章、錯誤排查技巧以及指南,旨在幫助IB客戶管理其IB賬戶。只需在搜索按鈕輸入您想要了解的內容,您便會得到答案。
3. 賬戶管理
我們的交易平台可供您訪問市場,賬戶管理則可供您訪問自己的IB賬戶。使用賬戶管理可管理賬戶相關任務,如存入或取出資金、查看您的報表、修改市場數據與新聞訂閱、更改交易許可并驗證或更改您的個人信息。
登錄賬戶管理 / 賬戶管理快速入門指南 / 賬戶管理用戶指南
4. 安全登錄系統
為向您提供最高級別的在線安全,盈透證券推出了安全登錄系統(SLS),通過安全登錄系統訪問賬戶需要進行雙因素驗證。雙因素驗證旨在于登錄時採用兩項安全因素確認您的身份:1) 您的用戶名與密碼組合;和2) 生成隨機、一次性安全代碼的安全設備。因為登錄賬戶需要既知曉您的用戶名/密碼又持有實物安全設備,所以參加安全登錄系統基本上可以杜絕除您以外的其他任何人訪問您賬戶的可能性。
如何激活您的安全設備 / 如何獲取安全代碼卡 / 如何退還安全設備
如果忘記密碼或丟失安全代碼卡,請聯繫我們獲取即時幫助。
5. 報表與報告
我們的報表與報告方便查看和進行自定義,覆蓋了您盈透賬戶的方方面面。如何查看活動報表
