Factor Certificates Tutorial
Introduction
Factor certificates employ a daily leverage factor that multiplies the daily performance of the underlying instrument. Unlike knock-out warrants and mini-futures, factor certificates do not have a knock-out barrier. To avoid a loss greater than the investment, the calculation resets intraday if the performance of the underlying threatens to render the certificate worthless.
Daily Leverage
The performance of the certificate is calculated daily, without reference to previous days’ values. If the underlying returns 1% on the day, the value of 3x certificate increases by 3%, a 5x by 5%. The next day the process is repeated, referencing the prior day’s underlying close.
As such, factor certificates are particularly suitable for day-traders.
However, for a period of more than one day, the cumulative performance of the underlying cannot be simply multiplied by a factor of 3 as the previous day’s price always forms the new basis of calculating each day’s performance for the certificate. To illustrate with an example:
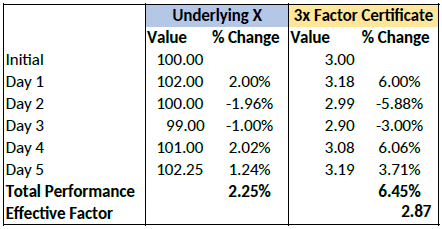
Cumulatively, the factor certificate has returned less than 3x the performance of the underlying.
Intraday Reset
If an underlying for a factor certificate loses more than a certain percentage of its value intraday, the calculation is reset by simulating a new day. The reset threshold varies depending on the leverage factor.
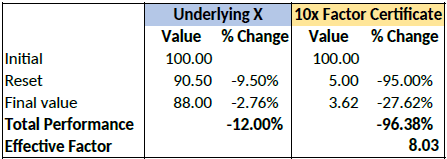
Let’s assume a long factor certificate with a 10x leverage factor. According to the terms of the certificate, a reset will be triggered if the underlying loses more than 9.5% during the calculation day.
Let’s now assume that the underlying loses 12% of its value during a particular day. The reset
and final performance will be as follows:
Overview of Central Bank of Ireland CFD Rules Implementation for Retail Clients at IBIE
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The Central Bank of Ireland (CBI) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2019. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR has implemented the CBI Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 Margins
Leverage limits were set by CBI at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for:
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g., USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- Gold
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the CBI Margins, IBKR establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by CBI .
Details of applicable IB and CBI margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD and/or Stock positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement for the combined Stock and CFD positions. Note that the concentration charge is the only instance where CFD and Stock positions are margined together.
1.3 Funding of Initial Margin Requirements
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position.
Initially all cash used to fund the account is available for CFD trading. Any initial margin requirements for other instruments and cash used to purchase cash stock reduce the available cash. If your cash stock purchases have created a margin loan, no funds are available for CFD trades even if your account has significant equity. We cannot increase a margin loan to fund CFD margin under the CBI rules.
Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
The CBI requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes CFD cash and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative). Note that CFD cash excludes cash supporting margin requirements for other instruments.
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your account and no open positions. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
|
|
Cash |
Equity* |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Pre Trade |
2000 |
2000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2000 |
|
|
Post Trade 1 |
2000 |
2000 |
50 |
100 |
5000 |
0 |
1000 |
500 |
1000 |
No |
|
Post Trade 2 |
2000 |
2000 |
100 |
100 |
10000 |
0 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the CBI rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
3000 |
100 |
110 |
11000 |
1000 |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
1500 |
100 |
95 |
9500 |
(500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
|
|
Cash |
Equity |
Position |
Price |
Value |
Unrealized P&L |
IM |
MM |
Available Cash |
MM Violation |
|
Change |
2000 |
500 |
100 |
85 |
8500 |
(1500) |
2000 |
1000 |
0 |
Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The CBI Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g., shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore, non-CFD assets are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading.
Should you lose more than the cash dedicated to CFD trading, IB must write off the loss.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
Концентрационная маржа по CFD, устанавливаемая IBKR для розничных клиентов
Плата за концентрацию действует для портфеля, если он состоит из малого числа позиций по CFD или две его крупнейшие позиции имеют главный вес. Мы воздействуем на портфель, используя гипотетический неблагоприятный сдвиг в 60% для двух крупнейших позиций и в 10% для остальных. Если общий рассчитанный убыток превышает стандартную маржу, то он устанавливается в качестве начального маржинального требования.
Однако во избежание завышенных маржинальных требований к относительно мелким позициям действует рибейт в USD 100 тыс. по начальной концентрационной марже (результат не может быть отрицательным);
ПрименяемаяКонцентрациионная = Макс(РассчитаннаяКонцентрационная - USD 100тыс.).
По предписаниям ESMA минимальная маржа составляет 50% от применямой концентрационной маржи.
Рибейт служит для устранения концентрационного сбора за позиции, находящиеся в пределах USD 250 тыс. (или эквивалента в другой валюте). Затем сбор будет постепенно увеличиваться, т.е., к примеру, для концентрированной позиции на USD 500 тыс. действует начальная маржа в 40%, а для позиции в 1 млн. - 50%. Данные примеры предполагают, что у клиента максимум 2 позиции; дополнительные позиции снизят общую плату.
Примеры (применяемая маржа выделена жирным шрифтом)
Только концентрированные позиции
1. Малый размер, концентрационный сбор устранен
| Начальная маржа | Плата за концентрацию | Стандарт | |||
| Позиция | USD | USD | % | USD | % |
| 1 | 100,000 | 60,000 | 60% | 20,000 | 20% |
| 2 | 50,000 | 30,000 | 60% | 15,000 | 30% |
| Всего | 150,000 | 90,000 | 60% | 35,000 | 23% |
| После рибейта | 0 | 0% |
2. Концентрационный сбор применяется по сниженной ставке
| Начальная маржа | Плата за концентрацию | Стандарт | |||
| Позиция | USD | USD | % | USD | % |
| 1 | 250,000 | 150,000 | 60% | 50,000 | 20% |
| 2 | 150,000 | 90,000 | 60% | 45,000 | 30% |
| Всего | 400,000 | 240,000 | 60% | 95,000 | 24% |
| После рибейта | 140,000 | 35% |
Дополнительные позиции
3. Концентрационный сбор снижается дополнительными позициями
| Начальная маржа | Плата за концентрацию | Стандарт | |||
| Позиция | USD | USD | % | USD | % |
| 1 | 250,000 | 150,000 | 60% | 50,000 | 20% |
| 2 | 150,000 | 90,000 | 60% | 45,000 | 30% |
| 3 | 100,000 | 10,000 | 10% | 20,000 | 20% |
| 4 | 50,000 | 5,000 | 10% | 10,000 | 20% |
| 5 | 50,000 | 5,000 | 10% | 10,000 | 20% |
| 6 | 50,000 | 5,000 | 10% | 10,000 | 20% |
| Всего | 650,000 | 265,000 | 41% | 145,000 | 22% |
| После рибейта | 165,000 | 25% |
Предупреждение о рисках
CFD - это комплексные контракты, несущие высокий риск денежных потерь ввиду кредитного плеча.
67% счетов розничных инвесторов терпят убытки, торгуя CFD через IBKR (UK).
Вам следует убедиться, что Вы понимаете принцип работы CFD и можете позволить себе подвергнуть Ваш капитал такому риску.
Общие сведения о моделях рынка CFD
Рынки внебиржевых контрактов на разницу (англ. Contracts For Difference или CFD), как правило, оперируют согласно одной из трех моделей: Прямой рыночный доступ (Direct Market Access или DMA), Брокер-агент (Agency Broker) или Маркет-мейкер (Market Maker).
IB использует модель DMA - самую прозрачную из трех. В случае данной модели поставщик сразу же хеджирует CFD-ордер через базовый наличный рынок, после чего CFD исполняется по цене хеджа. Это повышает прозрачность цен, и оплата услуг поставщика, как правило, основывается лишь на комиссионном сборе, а не надбавке или скидке.
Благодаря модели DMA профессионально ориентированные клиенты IB могут добавлять котировки в биржевую книгу, - точно так же, как и при торговле акциями. Поскольку IB сразу сопоставляет ордера на CFD с хедж-ордером, то нерыночные ордера CFD приводят к созданию соответствующих нерыночных ордеров на андерлаинг на бирже. Клиенты могут увидеть "свой" ордер в книге 2-го уровня.
Помимо этого все ордера (независимо от того, рыночные они или нет) пользуются преимуществом технологии Smart-маршрутизации IB, которая обеспечивает самое выгодное исполнение, направляя ордер на один из базовых рынков (LSE, CHI-X, Turquoise, BATS или внутреннее сопоставление с ордерами других клиентов).
Модель брокера-агента очень похожа на модель DMA тем, что ордера хеджируются напрямую через наличный рынок. Тем не менее при такой модели участники не видят свои лимитные ордера на бирже, поскольку они хранятся у поставщика и передаются, только когда становятся реализуемыми.
При традиционной же модели маркет-мейкера поставщик CFD включает все ордера в свою книгу заявок и по собственному усмотрению хеджирует или компенсирует сделку посредством опционов, варрантов, фьючерсов или через сам базовый рынок. Поставщик часто рекламируется как не взимающий комиссии. Тут цены меняются согласно его собственному механизму ценообразования, и он извлекает выгоду посредством ввода надбавки к спреду бида-аска. Эта модель часто ассоциируется с повышенным разбросом цен на неустойчивых рынках, а также с вероятностью пересмотра котировок.
Реализация правил ESMA в отношении CFD в IBKR – розничные клиенты
|
CFD – это сложные инструменты, которые сопряжены с высоким риском убытков из-за использования кредитного плеча.
63,7% счетов розничных инвесторов терпят убытки при торговле CFD через IBKR.
Убедитесь, что Вы понимаете принцип работы CFD и в состоянии принять на себя высокий риск убытков. |
Европейская служба по ценным бумагам и рынкам (ESMA) ввела новые правила по CFD для розничных клиентов, вступившие в силу 1 августа 2018 года. Они не распространяются на профессиональных клиентов.
В правила входят: 1) ограничения кредитного плеча; 2) правило ликвидации согласно марже конкретного счета; 3) защита счета от отрицательного баланса; 4) ограничение поощрительных программ по торговле CFD; и 5) стандартное предупреждение о рисках.
Большинство клиентов (за исключением регулируемых юр. лиц) изначально классифицируются как розничные. В некоторых случаях IBKR может согласиться изменить статус розничного клиента на профессиональный или наоборот. Подробнее можно узнать в статье "Классификация MiFID".
В следующих разделах описывается, как решение ESMA реализуется в IBKR (UK).
1. Ограничения кредитного плеча
1.1. Маржа ESMA.
ESMA установила ограничения кредитного плеча, которые зависят от базисного актива:
- 3,33% для основных валютных пар. Основные валютные пары – это любые комбинации USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY.
- 5% для прочих валютных пар и основных индексов;
- Прочие (не основные) валютные пары – это комбинации, в которые входит валюта, не указанная выше (например, USD.CNH)
- Основные индексы: IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- 10% для прочих фондовых индексов: IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% для отдельных акций
1.2. Применяемая маржа – стандартные требования.
Вдобавок к марже ESMA компания IBKR (UK) устанавливает свои собственные минимальные маржинальные требования ("Маржа IB") согласно исторической волатильности андерлаинга и прочим факторам, описанным ниже.Маржа IB применяется, если она выше предписанной ESMA.
Подробнее о действующих маржинальных требованиях IB и ESMA можно узнать здесь.
1.2.1. Применяемая маржа – минимальный уровень концентрации.
С портфеля взимается плата за концентрацию, если он состоит из малого числа позиций с CFD или его основной вес приходится на две крупнейшие позиции. Мы проводим тест для портфеля, моделируя неблагоприятный сдвиг в 30% для двух крупнейших позиций и в 5% – для остальных. Если общий убыток превышает стандартную маржу, то он устанавливается в качестве минимального маржинального требования.
1.3. Средства, доступные для начальной маржи.
Выполнение начальных маржинальных требований при открытии позиции по CFD возможно только за счет денежных средств. Реализованная прибыль по CFD включается в денежный остаток и становится доступна сразу – расчета ждать не нужно. В то же время нереализованная прибыль не может использоваться для покрытия начальной маржи.
1.4. Автоматическое финансирование начальных маржинальных требований (сегменты с приставкой "F").
IBKR (UK) автоматически переводит средства с Вашего основного счета на сегмент с приставкой "F", чтобы покрыть начальные маржинальные требования по CFD.
Обращаем внимание, что для удовлетворения дальнейших минимальных требований по CFD мы не совершаем таких переводов. Поэтому, если на этом сегменте недостаточно необходимых средств для покрытия маржи (см. ниже), то позиции будут ликвидированы независимо от того, достаточно ли средств на Вашем основном счете. Во избежание ликвидации Вам необходимо самостоятельно перевести дополнительные средства на F-сегмент на "Портале клиентов".
2. Правило ликвидации
2.1. Расчет минимальной маржи и ликвидация.
Согласно правилам ESMA, IBKR обязана ликвидировать CFD-позиции до того, как доступный остаток на счете опустится ниже 50% от начальной маржи, внесенной при открытии этих позиций. IBKR может закрыть позиции раньше, если внутренние правила в отношении риска являются более строгими. В рассматриваемый для этих целей остаток входят денежные средства на сегменте счета с приставкой "F" (средства на любых других сегментах не включаются) и нереализованная ПиУ по CFD-контрактам (положительная и отрицательная).
Основой расчета служат начальные маржинальные требования, действовавшие при открытии позиции по CFD. Другими словами, в отличие от расчетов маржи других продуктов, сумма начальной маржи для СFD не меняется при росте/снижении стоимости соответствующих открытых позиций.
2.1.1. Пример.
Денежный остаток на Вашем счете с CFD составляет 2000 EUR . Вы хотите купить 100 CFD на XYZ по лимитной цене в 100 EUR. Сначала выполняется покупка первых 50 CFD, а затем оставшихся 50. Сумма Ваших доступных средств уменьшается по мере исполнения:
| Наличные средства | Капитал* | Позиция | Цена | Стоимость | Нереализ. ПиУ | НМ | ММ | Доступные средства | Нарушение ММ | |
| Перед сделкой | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | |||||||
| После сделки 1 | 2000 | 2000 | 50 | 100 | 5000 | 0 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 | Нет |
| После сделки 2 | 2000 | 2000 | 100 | 100 | 10000 | 0 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Нет |
*Капитал – это денежный остаток (наличные) плюс нереализованная ПиУ.
Цена вырастает до 110. Теперь Ваш капитал равен 3000, но Вы не можете открывать дополнительные позиции, поскольку Ваши доступные денежные средства все еще составляют 0, и, согласно правилам ESMA, начальная и минимальная маржа не меняются.
| Наличные средства | Капитал | Позиция | Цена | Стоимость | Нереализ. ПиУ | НМ | ММ | Доступные средства | Нарушение ММ | |
| Изменение | 2000 | 3000 | 100 | 110 | 11000 | 1000 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Нет |
Затем цена опускается до 95. Ваш капитал снижается до 1500, что не нарушает требования маржи, поскольку он все еще превышает 1000:
| Наличные средства | Капитал | Позиция | Цена | Стоимость | Нереализ. ПиУ | НМ | ММ | Доступные средства | Нарушение ММ | |
| Изменение | 2000 | 1500 | 100 | 95 | 9500 | (500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Нет |
Цена снова снижается до 85, что приводит к нарушению маржинальных требований и ликвидации:
| Наличные средства | Капитал | Позиция | Цена | Стоимость | Нереализ. ПиУ | НМ | ММ | Доступные средства | Нарушение ММ | |
| Изменение | 2000 | 500 | 100 | 85 | 8500 | (1500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Да |
3. Защита от отрицательного капитала
Решение ESMA ограничивает Вашу ответственность по контрактам CFD до суммы, выделенной на сделки с ними. Для устранения дефицита маржи CFD не могут быть ликвидированы другие финансовые инструменты (например, акции или фьючерсы)*.
Поэтому активы на сегментах ценных бумаг и товаров Вашего основного счета, а также активы на сегменте "F", не относящиеся к CFD, не подвергаются риску при торговле CFD. Однако все денежные средства на сегменте "F" могут использоваться для покрытия убытков, возникших в результате операций с CFD.
Поскольку защита от отрицательного капитала представляет дополнительный риск для IBKR, с розничных инвесторов будет взиматься дополнительная надбавка в 1% за позиции с CFD, переносимые на следующий день. Подробные ставки финансирования CFD можно найти здесь.
Хотя для покрытия недостающей маржи по CFD нельзя ликвидировать позиции с другими активами, позиции с CFD могут быть ликвидированы для устранения дефицита маржи других инструментов.
4. Поощрительные программы по CFD
ESMA запрещает денежные и некоторые другие формы вознаграждений, связанные с торговлей CFD. IBKR не предлагает никакие бонусные или другие поощрительные программы по CFD.
Overview of ESMA CFD Rules Implementation at IBKR (UK) - Retail Investors Only
|
CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage.
61% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with IBKR.
You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money. |
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) enacted new rules applicable to retail clients trading CFDs, effective 1st August 2018. Professional clients are unaffected.
The rules consist of: 1) leverage limits; 2) a margin close out rule on a per account basis; 3) negative balance protection on a per account basis; 4) a restriction on the incentives offered to trade CFDs; and 5) a standardized risk warning.
Most clients (excepting regulated entities) are initially categorised as Retail Clients. IBKR may in certain circumstances agree to reclassify a Retail Client as a Professional Client, or a Professional Client as a Retail Client. Please see MiFID Categorisation for further detail.
The following sections detail how IBKR (UK) has implemented the ESMA Decision.
1 Leverage Limits
1.1 ESMA Margins
Leverage limits were set by ESMA at different levels depending on the underlying:
- 3.33% for major currency pairs; Major currency pairs are any combination of USD; CAD; EUR; GBP; CHF; JPY
- 5% for non-major currency pairs and major indices;
- Non-major currency pairs are any combination that includes a currency not listed above, e.g. USD.CNH
- Major indices are IBUS500; IBUS30; IBUST100; IBGB100; IBDE40; IBEU50; IBFR40; IBJP225; IBAU200
- 10% for non-major equity indices; IBES35; IBCH20; IBNL25; IBHK50
- 20% for individual equities
1.2 Applied Margins - Standard Requirement
In addition to the ESMA Margins, IBKR (UK) establishes its own margin requirements (IB Margins) based on the historical volatility of the underlying, and other factors. We will apply the IB Margins if they are higher than those prescribed by ESMA.
Details of applicable IB and ESMA margins can be found here.
1.2.1 Applied Margins - Concentration Minimum
A concentration charge is applied if your portfolio consists of a small number of CFD positions, or if the three largest positions have a dominant weight. We stress the portfolio by applying a 30% adverse move on the three largest positions and a 5% adverse move on the remaining positions. The total loss is applied as the maintenance margin requirement if it is greater than the standard requirement.
1.3 Funds Available for Initial Margin
You can only use cash to post initial margin to open a CFD position. Realized CFD profits are included in cash and are available immediately; the cash does not have to settle first. Unrealized profits however cannot be used to meet initial margin requirements.
1.4 Automatic Funding of Initial Margin Requirements (F-segments)
IBKR (UK) automatically transfers funds from your main account to the F-segment of your account to fund initial margin requirements for CFDs.
Note however that no transfers are made to satisfy CFD maintenance margin requirements. Therefore if qualifying equity (defined below) becomes insufficient to meet margin requirements, a liquidation will occur even if you have ample funds in your main account. If you wish to avoid a liquidation you must transfer additional funds to the F-segment in Account Management.
2 Margin Close Out Rule
2.1 Maintenance Margin Calculations & Liquidations
ESMA requires IBKR to liquidate CFD positions latest when qualifying equity falls below 50% of the initial margin posted to open the positions. IBKR may close out positions sooner if our risk view is more conservative. Qualifying equity for this purpose includes cash in the F-segment (excluding cash in any other account segment) and unrealized CFD P&L (positive and negative).
The basis for the calculation is the initial margin posted at the time of opening a CFD position. In other words, and unlike margin calculations applicable to non-CFD positions, the initial margin amount does not change when the value of the open position changes.
2.1.1 Example
You have EUR 2000 cash in your CFD account. You want to buy 100 CFDs of XYZ at a limit price of EUR 100. You are first filled 50 CFDs and then the remaining 50. Your available cash reduces as your trades are filled:
| Cash | Equity* | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Pre Trade | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | |||||||
| Post Trade 1 | 2000 | 2000 | 50 | 100 | 5000 | 0 | 1000 | 500 | 1000 | No |
| Post Trade 2 | 2000 | 2000 | 100 | 100 | 10000 | 0 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
*Equity equals Cash plus Unrealized P&L
The price increases to 110. Your equity is now 3000, but you cannot open additional positions because your available cash is still 0, and under the ESMA rules IM and MM remain unchanged:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 3000 | 100 | 110 | 11000 | 1000 | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price then drops to 95. Your equity declines to 1500 but there is no margin violation since it is still greater than the 1000 requirement:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 1500 | 100 | 95 | 9500 | (500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | No |
The price falls further to 85, causing a margin violation and triggering a liquidation:
| Cash | Equity | Position | Price | Value | Unrealized P&L | IM | MM | Available Cash | MM Violation | |
| Change | 2000 | 500 | 100 | 85 | 8500 | (1500) | 2000 | 1000 | 0 | Yes |
3 Negative Equity Protection
The ESMA Decision limits your CFD-related liability to the funds dedicated to CFD-trading. Other financial instruments (e.g. shares or futures) cannot be liquidated to satisfy a CFD margin-deficit.*
Therefore assets in the security and commodity segments of your main account, and non-CFD assets held in the F-segment, are not part of your capital at risk for CFD trading. However, all cash in the F-segment can be used to cover losses arising from CFD trading.
As Negative Equity Protection represents additional risk to IBKR, we will charge retail investors an additional financing spread of 1% for CFD positions held overnight. You can find detailed CFD financing rates here.
*Although we cannot liquidate non-CFD positions to cover a CFD deficit, we can liquidate CFD positions to cover a non-CFD deficit.
4 Incentives Offered to trade CFDs
The ESMA Decision imposes a ban on monetary and certain types of non-monetary benefits related to CFD trading. IBKR does not offer any bonus or other incentives to trade CFDs.
Внебиржевые фьючерсы IBKR на металлы LME – Факты и частые вопросы
Введение
OTC-фьючерсы LME IBKR обеспечивают клиентов синтетическим доступом к Лондонской бирже металлов (англ. London Metal Exchange или LME), поддерживающей социальную ссуду и, как правило, закрытой для инвесторов, не являющихся ее членами.
Фьючерсы LME на металлы являются внебиржевыми (OTC) производными контрактами, контрагентом для которых выступает IBUK. OTC-фьючерсы LME сопоставляются с котируемыми на LME сопряженными фьючерсами в плане цены, размера лота, типа и характеристик, но при этом не являются зарегистрированными контрактами. Физическая доставка по ним не поддерживается.
Торговля OTC-фьючерсами LME IBKR происходит с Вашего маржевого счета, а поэтому Вы можете устанавливать длинные и короткие позиции с кредитными плечом. Ставки маржи соразмерны установленным LME. Как и у других фьючерсов они основываются на рисках (метод SPAN), а поэтому могут варьироваться. Текущая маржа находится в диапазоне 6-9% в зависимости от контракта.
Контракты
IBKR предлагает внебиржевые фьючерсы на следующие металлы с истечением в третью среду:
| Металл | Символ IB | Цена USD/ | Множитель |
| Высококачественный первичный алюминий | AH | Метрическая тонна | 25 |
| Первоклассная медь | CA | Метрическая тонна | 25 |
| Первичный никель | NI | Метрическая тонна | 6 |
| Стандартный свинец | PB | Метрическая тонна | 25 |
| Олово | SNLME | Метрическая тонна | 5 |
| Высококачественный цинк | ZSLME | Метрическая тонна | 25 |
Истечение в третью среду
LME поддерживает целый ряд контрактов, отвечающих нуждам физических трейдеров и субъектов хеджирования. Их принцип заключается в трехмесячных форвардах, используемых физическими тредейрами для точного сопоставления сделок хеджирования с их потребностями.
Контракты "третьей среды" являются месячными, как и фьючерсы, и поэтому лучше подходят финансовым трейдерам. Как следует из названия, эти контракты истекают в третью среду каждого календарного месяца, и, хоть они и рассчитываются на LME физически, IBKR осуществляет исключительно денежный расчет. Популярность контрактов "третьей среды" продолжает расти - они составляют 65% открытого интереса на LME.
Котировки и рыночные данные
IBKR получает котировки от LME (рыночные данные 2-го уровня) и не расширяет их. Каждый клиентский ордер сначала хеджируется на бирже, и OTC-ордер LME исполняется по цене сделки хеджирования.
Движение денежных средств
Суточная вариационная маржа и реализованная ПиУ по OTC-фьючерсам LME IBKR рассчитывается ежедневно как у стандартного фьючерса. В то же время движение денежных средств по андерлаингу на LME рассчитывается только по истечении контракта.
Маржа
Маржинальные требования OTC-фьючерсов LME IBKR равны требованиям базового контракта на бирже LME. LME применяет стандартный анализ риска портфеля (англ. Standard Portfolio Analysis или SPAN) для расчета маржи.
Как и для других фьючерсов, ставки маржи устанавливаются в виде абсолютной величины за контракт и обновляются ежемесячно.
Торговые разрешения
Вам потребуется активировать разрешение на торговлю металлами Великобритании в "Управлении счетом".
Рыночные данные
Вам потребуется подписка на London Metal Exchange 2-го уровня, цена которой сейчас составляет GBP 1.00.
Материалы по LME OTC
Списки продуктов и ссылки на детали контрактов
Комиссии
Маржинальные требования
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Что мне нужно, чтобы начать торговать фьючерсами LME OTC?
Вам требуется активировать разрешение на торговлю металлами Великобритании в "Управлении счетом". Если Ваш счет находится в IB LLC или в IB UK (и обслуживается IB LLC), то мы создадим новый сегмент счета (с тем же номером и дополнительной приставкой “F”). Получив подтверждение, Вы сможете начать торговлю. F-счет не нужно финансировать отдельно - средства для соответствия маржинальным требованиям будут автоматически переводиться с основного сегмента.
Как мои сделки и позиции по фьючерсам LME OTC отражаются в выписках?
Позиции находятся на обособленном сегменте, отличающемся от номера Вашего основного счета приставкой “F”.. Наша система поддерживает как раздельные, так и совмещенные выписки. Вы можете изменить настройки в соответствующем разделе "Управления счетом".
Какие меры по защите счета распространяются на торговлю фьючерсами LME OTC?
Фьючерсы LME OTC - это контракты, контрагентом которых является IB UK. Торговля ими не ведется на регулируемой бирже, а клиринг не производится в центральной клиринговой палате. Имея IB UK в качестве второй стороны Ваших сделок, Вы подвергаетесь финансовым и деловым рискам, включая кредитный риск, характерный торговле через IB UK. Стоит помнить, что средства клиентов, в том числе и институциональных, всегда полностью сегрегируются. Компания IB UK участвует в Программе Великобритании по компенсации в сфере финансовых услуг ("FSCS"), а также не является участницей Корпорации защиты фондовых инвесторов (“SIPC”).
Можно ли торговать фьючерсами LME OTC по телефону?
Нет. В исключительных случаях мы можем согласиться обработать ордер на закрытие по телефону, но ни в коем случае не открытие.
IBKR OTC Futures on LME Metals – Facts and Q&A
Introduction
IBKR LME OTC Futures provide clients synthetic access to the London Metal Exchange, a peer to peer exchange not generally available to non-member investors.
The LME OTC Futures are OTC derivative contracts with IBUK as the counterparty. The LME OTC Futures reference the corresponding LME future in terms of price, lot size, type and specification but are themselves not registered contracts. Physical delivery is not permitted.
IBKR LME OTC Futures are traded through your margin account, and you can therefore enter long as well as short leveraged positions. Margin rates equal those established by the LME. Like other futures they are risk-based (SPAN), and therefore variable. Current margins range between 6 and 9% depending on the contract.
Contracts
IBKR offers OTC Futures on the 3rd Wednesday expirations for the following metals:
| Metal | IBKR Symbol | Price USD/ | Multiplier |
| High Grade Primary Aluminium | AH | Metric Ton | 25 |
| Copper Grade A | CA | Metric Ton | 25 |
| Primary Nickel | NI | Metric Ton | 6 |
| Standard Lead | PB | Metric Ton | 25 |
| Tin | SNLME | Metric Ton | 5 |
| Special High Grade Zinc | ZSLME | Metric Ton | 25 |
3rd Wednesday Expirations
The LME features a range of contracts adapted to the needs of physical traders and hedgers. The principal among them are daily 3-month forwards used by physical traders to precisely match their hedges to their needs.
The 3rd Wednesday contracts are monthly contracts, like futures, and as such better adapted to the needs of financial traders. As the name suggests, they expire on the 3rd Wednesday of each month and, although physically settled on the LME, are strictly cash-settled at IBKR. The 3rd Wednesday contracts have become increasingly popular and account for 65% of open interest on the LME.
Quotes and Market Data
IBKR streams quotes from the LME (L2 market data) and does not widen the quote. Every client order is first hedged on exchange and the LME OTC order filled at the price of the hedge.
Cash Flows
Daily variation margin and realized P&L for the IBKR LME OTC Futures are cash-settled daily, like a standard future. By contrast, cash flows for the underlying LME contract are only settled after the contract has expired.
Margins
The margin requirements for the IBKR LME OTC Futures equal the requirement for the underlying contract on the LME. LME uses Standard Portfolio Analysis of Risk (SPAN) to calculate Initial Margin.
Like for other futures, the margin rates are established as an absolute value per contract and usually updated monthly.
Trading Permissions
You will need to set up permissions for United Kingdom Metals in Client Portal.
Market Data
You will need a subscription for Level II London Metal Exchange, currently GBP 1.00.
LME OTC Resources
Product Listings & Links to Contract Details
Commissions
Margin Requirements
Frequently asked Questions
What do I need to do to start trading LME OTC Futures?
You need to set up trading permission for United Kingdom Metals in Client Portal. If you have an IB LLC or an IB UK account carried by IB LLC we will set up a new account segment (identified with your existing account number plus the suffix “F”). Once the set-up is confirmed you can begin to trade. You do not need to fund the F segment separately; funds will be automatically transferred from your main account to meet margin requirements.
How are my LME OTC Futures trades and positions reflected in my statements?
Your positions are held in a separate account segment identified by your primary account number with the suffix “F”. You can choose to view Activity Statements for the F-segment either separately or consolidated with your main account. You can make the choice in the statement window in Client Portal.
What account protections apply when trading LME OTC Futures?
LME OTC Futures are contracts with IB UK as your counterparty, and are not traded on a regulated exchange and are not cleared on a central clearinghouse. Since IB UK is the counterparty to your trades, you are exposed to the financial and business risks, including credit risk, associated with dealing with IB UK. Please note however that all client funds are always fully segregated, including for institutional clients. IB UK is a participant in the UK Financial Services Compensation Scheme ("FSCS"). IB UK is not a member of the U.S. Securities Investor Protection Corporation (“SIPC”).
Can I trade LME OTC Futures over the phone?
No. In exceptional cases we may agree to process closing orders over the phone, but never opening orders.
Overview of Forex CFDs issued by IB Australia - Facts and Q&A
The following article is intended to provide a general introduction to forex-based Contracts for Differences (CFDs) issued by IB Australia (IBA).
Transparent DMA Quotes: IBA ensures tight spreads and substantial liquidity as a result of combining quotation streams from 14 of the world's largest foreign exchange dealers which constitute more than 70% of market share in the global interbank market*. This results in displayed quotes as small as 0.1 PIP. IBA does not mark up the quotes, rather passes through the prices that it receives and charges a separate low commission.
*Source: Euromoney FX survey FX Poll 2016.
Carry Interest: Forex CFDs are rolled over reflecting the benchmark interest rate differential of the relevant currency pair. This is in principle similar to the TOM Next rolls used by other brokers, but offers greater stability as benchmark rates generally are less volatile than swap rates. In addition IBA applies a low financing spread that for major pairs starts at just 1.0% and can be as low as 0.5% for large balances. More volatile pairs have higher financing spreads.
The carry interest for IBA Forex CFDs is based on a currency-pair specific benchmark and a spread. The benchmark is the difference between the IBA benchmark rates for the two currencies. It is calculated as + BM Base currency – BM Quote currency.
For example, April 21, 2016 the GBP benchmark rate was 0.483%, the USD rate was 0.37%. The applicable benchmark rate is:
GBP.USD BM +0.48% - 0.37% = +0.113%
The applicable customer rate is Pair BM – IBA spread for long positions, BM + spread for short positions:
GBP.USD Long Rate +0.113% - 1.00% = -0.887%
GBP.USD Short Rate +0.113% + 1.00% = +1.113%
It is important to note that the long rate is applied as a credit, the short rate as a debit. Consequently for a long position a positive rate means a credit, a negative rate a charge. However for short positions a positive rate means a charge, a negative rate a credit.
Interest is calculated on the contract value expressed in the quote currency, and credited or debited in that currency if it is either AUD or USD. Interest in other currencies is converted into the base currency of your account and then credited or debited.
For example:
| Daily Interest | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | GBP.USD Close | USD Value | Rate | USD | |
| GBP.USD | -20,000 | 1.43232 | -28,646.40 | 1.113% | -0.89 |
Interest on Forex CFD balances is calculated on a stand-alone contract basis, and not combined or netted with other currency exposures, including Spot FX. Although IBA does not directly reference swap rates, IBA reserves the right to apply higher spreads in exceptional market conditions, such as during spikes in swap rates that can occur around fiscal year-ends.
Detailed interest schedules can be viewed here.
Trading: IBA Forex CFDs can be traded either in classical TWS or in the IBA FX Trader, with over 20 available order types and algos. To find the contract you want to trade in classical TWS or FX Trader, enter the currency pair (i.e. EUR.USD) and choose Sec Type CFD in the Contract Selection pop-up.
Margin: IBA Forex CFD margins are determined for each currency pair on a per contract basis without regard to other Forex balances held in the account. Margins start as low as 2.5% of contract value for major currency pairs. Details for all currency pairs can be found here.
Commissions: IBA passes through the prices that it receives and charges a separate low commission. We do this in the interest of providing a transparent pricing structure instead of marking up our quotes and charging nothing in commissions as is the practice with many forex brokers. Commissions are tiered based on monthly traded value, and range from 0.20 basis points to 0.08 basis points.
Details are found here.
Trading Permissions: In order to trade Forex CFDs, you must set up the trading permission for Forex CFDs in Account Management. The suitability criteria are the same as those for Leverage FX. Share and Index CFDs are a separate trading permission.
Trading Example
Opening the position
You purchase 10 lots (200000) EUR.CHF CFDs at $1.16195 for CHF 232,390, which you then hold for 5 days.
| EUR.CHF Forex CFDs – New Position | |
|---|---|
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16188 - 1.16195 |
| Action | Buy |
| Quantity | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 232,390.00 |
| Margin (3% x 232,390) | AUD 9,100 |
| Interest Charged (on CHF 232,390 over 5 days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I (Pair BM 0.42% - IB Spread 1%) | CHF 232,390.00 | -0.58% | (CHF 18.72) |
Closing the position
| Exit CFD Position | ||
|---|---|---|
| Profit Scenario | Loss Scenario | |
| Reference Underlying Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| CFDs Reference Price | 1.16840 - 1.16848 | 1.15539 - 1.15546 |
| Action | Sell | Sell |
| Quantity | 200,000 | 200,000 |
| Trade Value | CHF 233,680.00 | CHF 231,078.00 |
| Trade P&L | CHF 1,290.00 | (CHF 1,312.00) |
| Financing | (CHF 18.72) | (CHF 18.72) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.65) | (CHF 4.65) |
| Entry Commission 0.002% | (CHF 4.67) | (CHF 4.62) |
| Total P&L | CHF 1,261.96 | (CHF 1,339.99) |
| Total P&L @ AUD.CHF 0.770855 | AUD 1,637.09 | (AUD 1,738.32) |
CFD Resources
Below are some useful links with more detailed information on IBA’s CFD offering:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between IBA Forex CFDs and other forms of forex trading?
IBA Forex CFDs are differentiated mainly by their their exceptionally tight spreads resulting from that IBA a) combines quotation streams from 14 of the world's largest foreign exchange dealers which constitute more than 70% of market share in the global interbank market*. This results in displayed quotes as small as 0.1 PIP, and b) IBA does not mark up the quotes, rather passes through the prices that it receives and charges a separate low commission.
*Source: Euromoney FX survey FX Poll 2016.
IBA Forex CFDs also offer a unique financing model for positions held overnight. IBA uses a pair benchmark rate which is the difference between the benchmark rates for the two underlying currencies. This is in principle similar to the TOM Next rolls used by other brokers, but offers greater stability as benchmark rates generally are less volatile than swap rates.
Please see the Carry Interest section above for a detailed example.
Are there any market data requirements?
The market data for IBA Forex CFDs is the same as for Leverage FX. It is a global permission and free of charge.
Related Articles
Overview of Share CFDs issued by IB Australia
Share CFD Definition
IBA CFDs are OTC contracts which deliver the return of the underlying stock, including dividends and corporate actions (read more about CFD corporate actions). You can enter long as well as short leveraged positions.
Said differently, it is an agreement between the buyer (you) and IBA to exchange the difference in the current value of a share, and its value at a future time. If you hold a long position and the difference is positive, IBA pays you. If it is negative, you pay IBA.
IBA’s CFDs work on an Open Trade Equity model. With IBA’s CFDs, the Open Trade Equity (OTE) represents the cumulative unrealised profit/loss on the CFD position relative to movements in the current price of the Reference Underlying. The profit/loss is realised when the position is closed. If the profit/loss is in a currency other than AUD or USD it is converted to the base currency of your account and credited/debited to cash.
The price of the CFD is the exchange-quoted price of the underlying share. In fact, IBA CFD quotes are identical to the Smart-routed quotes for shares that you can observe in the Trader Work Station and IBA offers Direct Market Access (DMA). Similar to shares, your nonmarketable (i.e., limit) orders have the underlying hedge directly represented on the deep book of those exchanges at which it trades. This also means that you can place orders to buy the CFD at the underlying bid and sell at the offer.
To compare IBA’s transparent CFD model to others available in the market please see our Overview of CFD Market Models.
IBA currently offers approximately 6200 Share CFDs covering the principal markets in the US, Europe and Asia. The constituents of the major indexes listed below are currently available as IBA Share CFDs. In many countries IBA also offers trading in liquid small cap shares. These are shares with free float adjusted market capitalization of at least USD 500
million and median daily trading value of at least USD 600 thousand. Please see CFD Product Listings for more detail. More countries will be added in the near future.
| United States | S&P 500, DJA, Nasdaq 100, S&P 400 (Mid Cap), Liquid Small Cap |
| United Kingdom | FTSE 350 + Liquid Small Cap (incl. IOB) |
| Germany | Dax, MDax, TecDax + Liquid Small Cap |
| Switzerland | Swiss portion of STOXX Europe 600 (48 shares) + Liquid Small Cap |
| France | CAC Large Cap, CAC Mid Cap + Liquid Small Cap |
| Netherlands | AEX, AMS Mid Cap + Liquid Small Cap |
| Belgium | BEL 20, BEL Mid Cap + Liquid Small Cap |
| Spain | IBEX 35 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Portugal | PSI 20 |
| Sweden | OMX Stockholm 30 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Finland | OMX Helsinki 25 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Denmark | OMX Copenhagen 30 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Norway | OBX |
| Czech | PX |
| Japan | Nikkei 225 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Hong Kong | HSI + Liquid Small Cap |
| Australia | ASX 200 + Liquid Small Cap |
| Singapore* | STI + Liquid Small Cap |
*not available to Singapore residents
Comparison Between CFDs and Underlying Shares
Depending on your trading objectives and trading style, CFDs offer a number of advantages compared to stocks, but also some disadvantages:
| Benefits of IB CFDs | Drawbacks of IB CFDs |
|---|---|
| No stamp duty or financial transaction tax (UK, France, Belgium) | No ownership rights |
| Generally lower commission and margin rates than shares | Complex corporate actions may not always be exactly replicable |
| Tax treaty rates for dividends without need for reclaim | Taxation of gains may differ from shares (please consult your tax advisor) |
| Exemption from day trading rules |
Worked Example
Opening the position:
You purchase 30,000 CFDs at $10.00 for $300,000, which you then hold for 30 days.
| AUD Share CFDs- New Position | |
|---|---|
| Reference Underlying Price | $9.98 - $10.00 |
| CFDs Reference Price | $9.98 - $10.00 |
| Action | Buy |
| Quantity | 30000 |
| Trade Value | $300,000 |
| Margin (20% x 300,000)1 | $60,000 |
| Interest tier Charged (on $300,000 over 30 days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tier I | $140,000 | 2.942% | $338.53 |
| Tier II 2 | $160,000 | 2.942% | $386.89 |
| Total Interest Charged | $725.42 | ||
Closing the position:
| Exit CFD Position | ||
|---|---|---|
| Profit Scenario | Loss Scenario | |
| Reference Underlying Price | $10.48 - $10.50 | $9.48 – $9.50 |
| CFDs Reference Price | $10.48 - 10.50 | $9.48 – 9.50 |
| Action | Sell | Sell |
| Quantity | 30,000 | 30,000 |
| Trade Value | $314,400 | $284,400 |
| Trade P&L | $14,400.00 | ($15,600.00) |
| Financing | ($725.42) | ($725.42) |
| Entry Commission 0.05% | ($150.00) | ($150.00) |
| Exit Commission 0.05% | ($157.20) | ($142.20) |
| Total P&L | $13,367.38 | ($16,617.62) |
1) Assuming minimum margin of 20%
2) IBA spread is 1.5% for all AUD tiers. Other currencies have additional tiers of 1%
and 0.5%
CFD Resources
Below are some useful links with more detailed information on IBA’s CFD offering:
CFD Contract Specifications
CFD Product Listings
CFD Commissions
CFD Financing Rates
CFD Margin Requirements
CFD Corporate Actions
The following video tutorial is also available:
How to Place a CFD Trade on the Trader Workstation
Frequently Asked Questions
What Stocks are available as CFDs?
Large and Mid-Cap stocks in the US, Western Europe, Nordic and Japan. Liquid Small Cap stocks are also available in many markets. Please see CFD Product Listings for more detail. More countries will be added in the near future.
Do you have CFDs on Other Underlying Types?
Yes. Please see IBA Index CFDs - Facts and Q&A and Forex CFDs - Facts and Q&A.
How do you determine your Share CFD quotes?
IBA CFD quotes are identical to the Smart routed quotes for the underlying share. IBA does not widen the spread or hold positions against you. To learn more please go to Overview of CFD Market Models.
Can I see my limit orders reflected on the exchange?
Yes. IBA offers Direct market Access (DMA) whereby your non-marketable (i.e., limit) orders have the underlying hedge directly represented on the deep book of those exchanges at which it trades. This also means that you can place orders to buy the CFD at the underlying bid and sell at the offer. In addition, you may also receive price improvement if another
client’s order crosses at a better price than is available on public venues.
How do you determine margins for Share CFDs?
IBA establishes risk-based margin requirements based on the historical volatility of each underlying share. The minimum margin is 20% for long positions, 25% for short positions. In addition IB applies a concemtration charge margining the two largest positions at 30%, standard margin applied to additional positions. There are no portfolio off-sets between individual CFD positions or between CFDs and exposures to the underlying share. A large position charge applies if the CFD position exceeds 0.5% of the market capitalisation of the underlying share. Please refer to CFD Margin Requirements for more detail.
Are short Share CFDs subject to forced buy-in?
Yes. In the event the underlying stock becomes difficult or impossible to borrow, the holder of the short CFD position will become subject to buy-in.
How do you handle dividends and corporate actions?
IBA will generally reflect the economic effect of the corporate action for CFD holders as if they had been holding the underlying security. Dividends are reflected as cash adjustments, while other actions may be reflected through either cash or position adjustments, or both. For example, where the corporate action results in a change of the number of shares (e.g. stocksplit, reverse stock split), the number of CFDs will be adjusted accordingly. Where the action results in a new entity with listed shares, and IBA decides to offer these as CFDs, then new long or short positions will be created in the appropriate amount. For an overview please CFD Corporate Actions.
Please note that in some cases it may not be possible to accurately adjust the CFD for a complex corporate action such as some mergers. In these cases IBA may terminate the CFD prior to the ex-date.
What do I need to do to start trading CFDs with IBA?
You need to set up trading permission for CFDs in Account Management, and agree to the relevant trading disclosures.
Are there any market data requirements?
The market data for IBA Share CFDs is the market data for the underlying shares. It is therefore necessary to have market data permissions for the relevant exchanges. If you already have set up market data permissions for an exchange for trading the shares, you do not need to do anything. If you want to trade CFDs on an exchange for which you do not
currently have market data permissions, you can set up the permissions in the same way as you would if you planned to trade the underlying shares.
Can I transfer in CFD positions from another broker?
IBA will be glad to facilitate the transfer of CFD positions, subject to the agreement of the other broker. As the transfer of CFD positions is more complex than is the case for share positions, we generally require the position to be at least the equivalent of USD 100,000.
Are charts available for Share CFDs?
Yes.
What account protections apply when trading CFDs with IBA?
CFDs are contracts with IBA as your counterparty, and are not traded on a regulated exchange and are not cleared on a central clearinghouse. Since IBA is the counterparty to your CFD trades, you are exposed to the financial and business risks, including credit risk, associated with dealing with IBA. IBA will handle the client money it receives in accordance
with the rules set out in Part 7.8 of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (Client Money Rules) and to the extent applicable the ASIC Market Integrity Rules (ASX market) 2010. Where required, IBA will pay such client money into a trust account. Please refer to the IBA CFD Product Disclosure Statement for further detail on risks associated with trading CFDs.
What are the maximum a positions I can have in a specific CFD?
There is no pre-set limit. Bear in mind however that very large positions may be subject to increased margin requirements. Please refer to CFD Margin Requirements for more detail.
Can I trade CFDs over the phone?
No. In exceptional cases we may agree to process closing orders over the phone, but never opening orders.
Related Articles
